US Personal Consumption Expenditure Price Index March Preview: Inflation is here
- Producer and consumer prices climb sharply in March.
- Federal Reserve cites temporary base effect for price gains.
- Inflation averaging has removed price changes from immediate Fed concern.
- PCE rates could rise more than expected in March.
- Dollar, markets will be unaffected by inflation readings.

American consumer prices are set to climb by the most in a year, and though larger increases lie ahead there will be no immediate impact on Fed monetary policy.
The Personal Consumption Expenditure Prices Index (PCE) is forecast to rise 0.3% in March from 0.2% in February and to be unchanged at 1.6% on the year. The Core PCE Price Index should gain 0.3% and 1.8% following February’’s 0.1% and 1.4% increases.
CPI, PPI and the base effect
The PCE Index is the last of the three major inflation gauges to report each month. It is the most recent in origin and the Federal Reserve’s preferred measure.
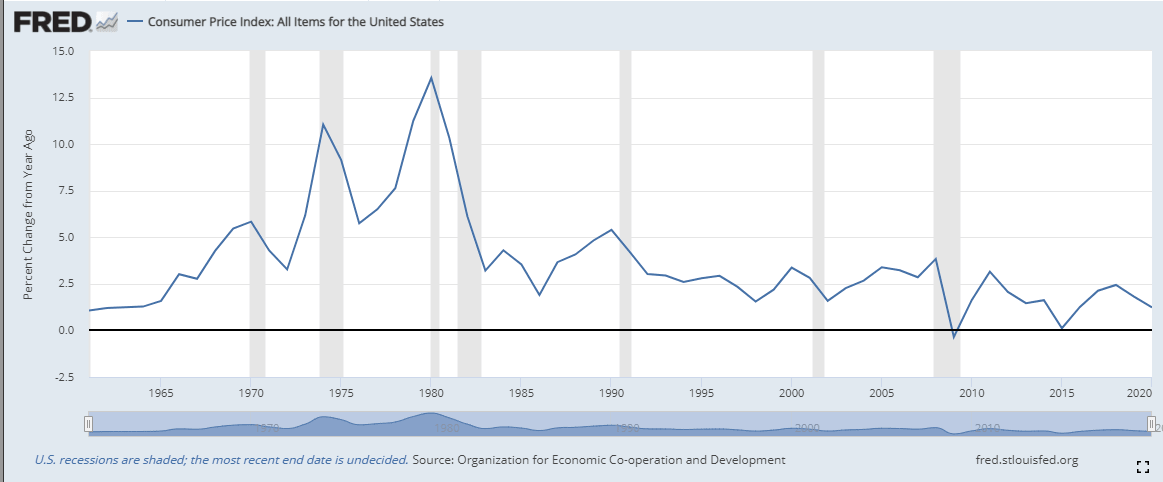
Last year’s March and April lockdowns collapsed consumer prices as sales plunged and retailers did all they could to move inventory.
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) dropped from a 2.3% annual rate in February 2020 to 1.5% in March, 0.3% in April and 0.1% in May. The core rate fell from 1.9% in February to 1.7% in March, 0.9% in April and 1% in May.
CPI
Producer prices saw the same drop in demand and response, though slightly earlier.
The annual Producer Price Index (PPI) tumbled from 2% in January 2020 to 1.1% in February, 0.3% in March and -1.5% in April. The Core PPI rate slipped from 1.6% in January to 1.2% in February, 1.1% in March and 0.3% in April.
Those highly unusual declines have reversed but the large gap in the underlying indexes between the lockdown months and the following year makes large increases a mathematical certainty.
For CPI the price index in March 2020 was 258.115, this year it was 264.877, which produces a 2.61% increase. In April 2020 the index fell to 256.389 and in May 256.394. Even if this year's index does not rise in April and May, the annual increase would still be 3.31% in April and 3.30% in May.
In Core CPI the biggest rate drop in 2020 occurred from March to April (1.7% to 0.9%, as above) and consequently, the largest rise will be next month.
Similar variations in the PPI facilitated the 2.8% February and 4.2% March gains this year with 2.5% and 3.1% increases in the Core PPI rate.
Personal Consumption Expenditure Price Index
Last year the PCE Price Index dropped from 1.8% in February to 1.3% in March and 0.5% in April. Given that 0.5% drop in last year’s March index the current consensus estimate for an unchanged rate this year at 1.6% last month seems too low.
The core rate in 2020 fell from 1.7% in March to 0.9% in April then rose to 1% in May. That 0.8% drop last March should result in a greater reversal than the 0.4% gain to 1.8% predicted this year.
Core PCE Price Index
FXStreet
Fed policy
Inflation has been a second-order Fed concern for more than a decade. Since the financial crisis employment has slowly evolved into the central policy goal, supplanting price stability in twin mandates for the central bank.
The Fed made this transposition official last September when it adopted inflation averaging as its policy guideline. The FOMC’s aim is to manage price increases so that inflation averages 2% over a prolonged but unspecified period.
This change means that the Fed, and perhaps, more importantly, the Treasury market, is not reactive to monthly variation in the inflation rate.
Fed Chair Jerome Powell has made it very plain, most recently in Wednesday’s press conference, that a fully recovered labor market is the goal.
Conclusion
Inflation is not just coming, it is here.
The March and subsequent expected increases are a product of the unusual plunge in prices during the lockdown months. Those gains will, as Mr Powell has often said, dissipate as the base index becomes more stable. They are temporary. By October last year, the consumer price index was again over 260, rising every month and diminishing the percentage gains to this year.
But that is not the only inflation consideration.
Commodity prices have risen sharply in the last few weeks. Part of the gain is due to lingering production shortages from the lockdowns, but rising demand for goods and services is also responsible.
As the US economy revs into the recovery those restraints on manufacturing combined with a surge in consumption threaten to change the price dynamic more than the transitory and limited base effect.
Underneath the surface price pressures is the vast pool of liquidity created by the Fed to fight the economic effects of the pandemic. Add to this the unprecedented spending pouring out of Washington under the Biden administration and you have circumstances that have not existed in the US since the funding debacle of the Vietnam War.
It took the Fed ten years to understand the cause of inflation in the 1970s and to implement a solution under Paul Volker and President Reagan.
If inflation returns, the Fed will not have to search for an answer.
Premium
You have reached your limit of 3 free articles for this month.
Start your subscription and get access to all our original articles.
Author

Joseph Trevisani
FXStreet
Joseph Trevisani began his thirty-year career in the financial markets at Credit Suisse in New York and Singapore where he worked for 12 years as an interbank currency trader and trading desk manager.