EUR/JPY dips further below 159.50 post ECB’s rate cut
- ECB's rate cut to 3% aims to anchor inflation closer to the 2% target amid ongoing economic challenges.
- Updated ECB forecasts suggest a gradual decline in inflation, with HICP expected to reach 1.9% by 2026.
- Market attention now turns to ECB President Christine Lagarde's upcoming press conference for further cues.

The Euro weakens against the Japanese Yen during the North American session after the European Central Bank (ECB) cut interest rates. At the time of writing, the EUR/JPY trades volatile within the 159.00-159.80 range.
EUR/JPY experiences volatility, after ECB slashes interest rates and updated its forecasts
The ECB lowered their three key interest rates by 25 bps, leaving the deposit rate at 3%. The monetary policy statement mentioned that the central bank is determined to drive inflation to its 2% goal, adding they’re not pre-committed toa particular rate path.
ECB officials added that the disinflation is “well on track” and despite evolving, inflation remains high.
In its meeting, the ECB updated its forecasts for inflation and economic growth. The Harmonised Index of Consumer Prices (HICP) for 2024 is expected to end at 2.4%, down from 2.5%. For 2025 and 2026, HICP is foreseen to end at 2.1% and 1.9%, respectively.
Core HICP is projected to finish the year at 2.9%, unchanged compared to the previous forecast, and for 2025 and 2026 is foreseen to dip to 2.3% and 1.9%, respectively.
The Gross Domestic Product is foreseen at 0.7% I n2024, at 1.1% in 2025 and 1.4% in 2026.
Following the monetary statement release, traders focus shifts to ECB’s President Christine Lagarde press conference at around 13:45 GMT.
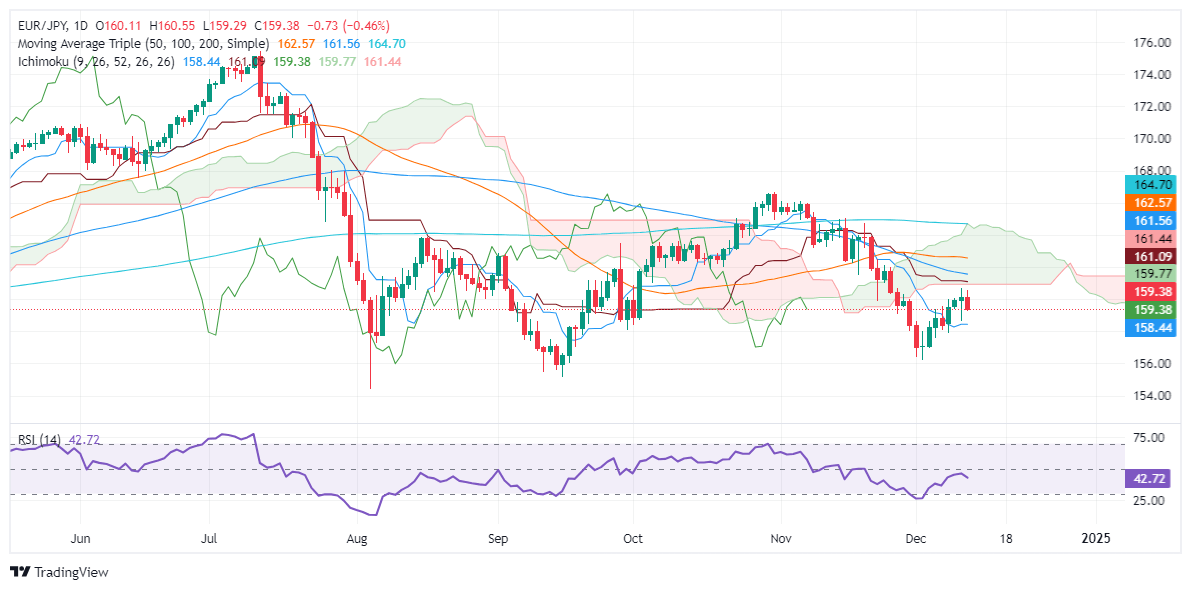
EUR/JPY Price Forecast: Technical outlook
The EUR/JPY extended its losses below 160.00, with traders eyeing a re-test of the December 11 low of 158.64. On further weakness, the cross-pair could dive towards the Tenkan-Sen at 158.45, before sliding to 158.00.
Conversely, if buyers push the exchange rate above 160.00, this could pave the way to test the Kijun-Sen at 161.07.
ECB FAQs
The European Central Bank (ECB) in Frankfurt, Germany, is the reserve bank for the Eurozone. The ECB sets interest rates and manages monetary policy for the region. The ECB primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which means keeping inflation at around 2%. Its primary tool for achieving this is by raising or lowering interest rates. Relatively high interest rates will usually result in a stronger Euro and vice versa. The ECB Governing Council makes monetary policy decisions at meetings held eight times a year. Decisions are made by heads of the Eurozone national banks and six permanent members, including the President of the ECB, Christine Lagarde.
In extreme situations, the European Central Bank can enact a policy tool called Quantitative Easing. QE is the process by which the ECB prints Euros and uses them to buy assets – usually government or corporate bonds – from banks and other financial institutions. QE usually results in a weaker Euro. QE is a last resort when simply lowering interest rates is unlikely to achieve the objective of price stability. The ECB used it during the Great Financial Crisis in 2009-11, in 2015 when inflation remained stubbornly low, as well as during the covid pandemic.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse of QE. It is undertaken after QE when an economic recovery is underway and inflation starts rising. Whilst in QE the European Central Bank (ECB) purchases government and corporate bonds from financial institutions to provide them with liquidity, in QT the ECB stops buying more bonds, and stops reinvesting the principal maturing on the bonds it already holds. It is usually positive (or bullish) for the Euro.
Author

Christian Borjon Valencia
FXStreet
Christian Borjon began his career as a retail trader in 2010, mainly focused on technical analysis and strategies around it. He started as a swing trader, as he used to work in another industry unrelated to the financial markets.