US Consumer Price Index April Preview: The two base effects of inflation
- Annual CPI expected to jump 3.6% in April .
- April 2020 had the lowest consumer price index of the pandemic.
- US Gasoline prices are up 43% in six months.
- Federal Reserve foresees no policy changes with inflation.

American consumer prices are set to rise by the most in decade as the base effect from last year’s pandemic collapse reaches its height.
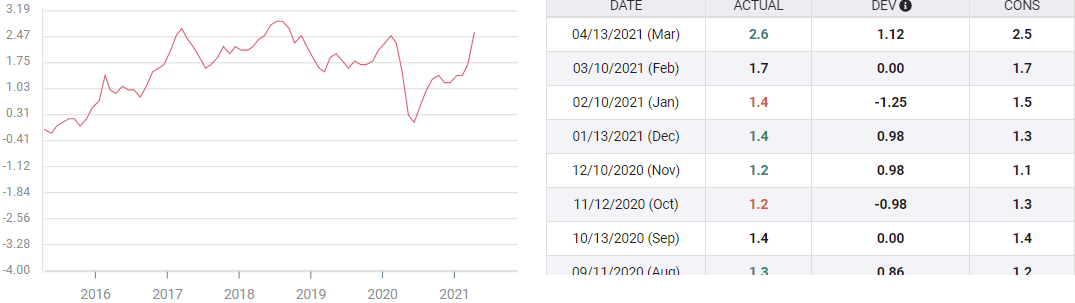
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is expected to climb 0.2% in April, according to the consensus forecast from the Reuters survey of economists. In March CPI rose 0.6%. Annual prices are projected to jump 3.6% following the 2.6% increase in March.
Core prices are predicted to be unchanged at 0.3% on the month but to rise 2.3% annually in April from 1.6% in March
Consumer Price Index
The Consumer Price Index tracks the change in cost for a basket of goods over time with a reference to a base year as 100.
Last year's lockdown in March and April crushed retailers who were forced to sell goods at discounts or not at all as most consumers limited their purchases to essential items and services.
As the shutdown took hold last spring the index dropped from 258.678 in February to 258.115 in March to the low of 256.389 in April 2020.
Consumer Price Index
Prices began to recover in May, and by July’s 259.101 score the index was above February's pre-lockdown level.
Since last July price increases have averaged 0.3% a month. By March those cumulative gains had produced an index level of 264.877, or 2.62% above the 258.115 last March.
The same comparison with the April 2020 index is projected to produce a 3.3% gain this year.
CPI
FXStreet
Consumer prices base effect vs demand shortage
The quickly reviving US economy and government pandemic largesse have invigorated consumption. Retail Sales averaged 4.8% for the first quarter, which, except for the May, June and July rebound from the prior collapse, was the strongest quarter for sales in two decades.
The rebound has exposed numerous shortages in goods and services, due to backorders, and scare components and materials. Prices have jumped for some goods and more increases are likely as the economy fully opens and normal life resumes.
In addition, energy costs, which factor into almost all consumer goods, have risen sharply since the presidential election last November.
A barrel of West Texas Intermediate (WTI), the North American pricing standard, has climbed 79.7% since it opened at $35.90 on November 2 the day before the vote.
WTI
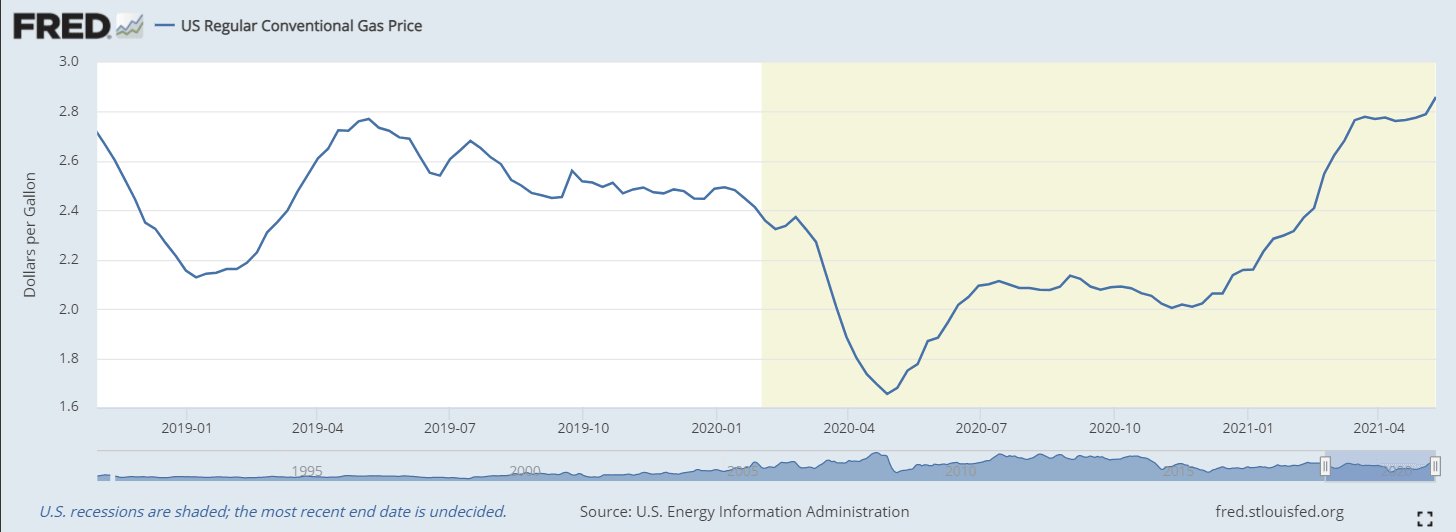
Gasoline prices have gone up in tandem. From a nationwide average of $2.02 a gallon on November 2, prices have climbed 43% to $2.86 on May 10. The gains are a compound of rising demand as the pandemic has waned and the Biden administration’s energy policy, which has eliminated all new oil production leases on federal land.
Federal Reserve inflation policy
The Federal Reserve anticipated the steep increases in the CPI this year when the governors adopted an inflation-averaging policy last September. Once economic recovery began the jump in CPI was a mathematical certainty as long as prices resumed a normal course.
This new guideline permits inflation to run above target for a long enough and unspecified period to generate a 2% overall average.
By this change the Fed has disabled its reaction function. In the past, inflation above 2% for more than a month or two, would have sent credit markets speculating about a rate increase.
The purpose of the new stipulation was to give the central bank much greater freedom to maintain accommodative rates, regardless of price variation.
Conclusion
Fed Chair Jerome Powell and other officials have said repeatedly that the current spate of price increases are a limited phenomenon, attributable largely to the base effect from last year's lockdown. In that they are correct. The March and April CPI jumps are transitory. These increases in CPI will not and should not tempt the governors into preventative rate measures.
But these are not the only factors operating on consumer prices. Demand is increasing for many consumer goods. For some, bicycles for instance, production delays and a shortage of parts are keeping supply limited.
Employers are beginning to offer higher wages because in many industries they cannot find enough workers.
This combination of rising retail demand, scarcity for some consumer goods and incipient wage gains may, if they continue, raise the base rate of consumer inflation expectations.
The Fed insists that all three problems are temporary, the products of manufacturing and labor shortages that will ease as the economy fully recovers.
For markets, whether the Fed’s inflation analysis proves accurate is, for the moment, irrelevant. There is no CPI result that will prompt speculation on interest rates.
Premium
You have reached your limit of 3 free articles for this month.
Start your subscription and get access to all our original articles.
Author

Joseph Trevisani
FXStreet
Joseph Trevisani began his thirty-year career in the financial markets at Credit Suisse in New York and Singapore where he worked for 12 years as an interbank currency trader and trading desk manager.