EUR/AUD edges higher despite bearish fundamentals
- EUR/AUD is rising despite a run of weak data from the Eurozone and lower inflation expectations.
- In comparison data from Australia has been relatively robust of late, particularly sentiment and wage data.
- Monetary policy is diverging with the ECB likely to cut interest rates further, leading to a bearish backdrop for EUR/AUD.

EUR/AUD is exchanging hands in the 1.6630s on Wednesday, up a third of a percent on the day. The pair has fallen about 3.3% in just over a week since the 1.7186 high reached on August 5. Despite the current uptick, the short-term trend is bearish and since “the trend is your friend” the pair is vulnerable to more downside.
EUR/AUD has weakened primarily due to an ebbing away of US recession fears which temporarily weakened the Australian Dollar (AUD) due to its sensitivity to negative risk sentiment. The differing outlooks for monetary policy of the two currencies and comparably resilient recent Australian macroeconomic data are further drivers of the pair’s decline since the August 5 high.
On Wednesday Eurostat released the latest Gross Domestic Product (GDP), Employment Change and Industrial Production for the Eurozone. The GDP was a second estimate for Q2 and showed no change from the preliminary reading, Employment Change for Q2 was likewise unchanged. Industrial Production in June, however, fell below expectations.
The future course of rates
Interest rates are a key driver of FX markets since international investors like to park their money where it can earn the highest return. This increases demand for currencies where interest rates are high. The difference marginally benefits the AUD since the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) has set a slightly higher policy rate of 4.35% compared to the 4.25% set by the European Central Bank (ECB). The difference is marginal, however, and more important perhaps is the expected trajectory of interest rates in the future.
The ECB cut interest rates for the first time in several years in June 2024, prior to that they stood at 4.50%. The bank has adopted a “wait-and-see” approach to interest rates based on how the Eurozone economy evolves and the inflation rate. If inflation continues to ease it will continue cutting interest rates to benefit commerce; if inflation remains stubbornly high it will keep interest rates unchanged until inflation comes down.
In Australia the position of the RBA is slightly different. The RBA is one of the few central banks (including the Federal Reserve) not to have begun cutting interest rates since the post Covid spike in inflation started to fall. It is also the only major central bank remaining that is threatening to actually raise interest rates (except the BoJ which is in a unique position) in the event that inflation continues creeping higher.
The difference in the monetary policy stances of the two banks is a backwind for the Aussie Dollar and a negative background factor for EUR/AUD.
Price trends
The stronger trend of decreasing inflation in the Eurozone also suggests that the ECB is more likely to cut interest rates again – possibly before the RBA even begins. Such a move would be bearish for EUR/AUD.
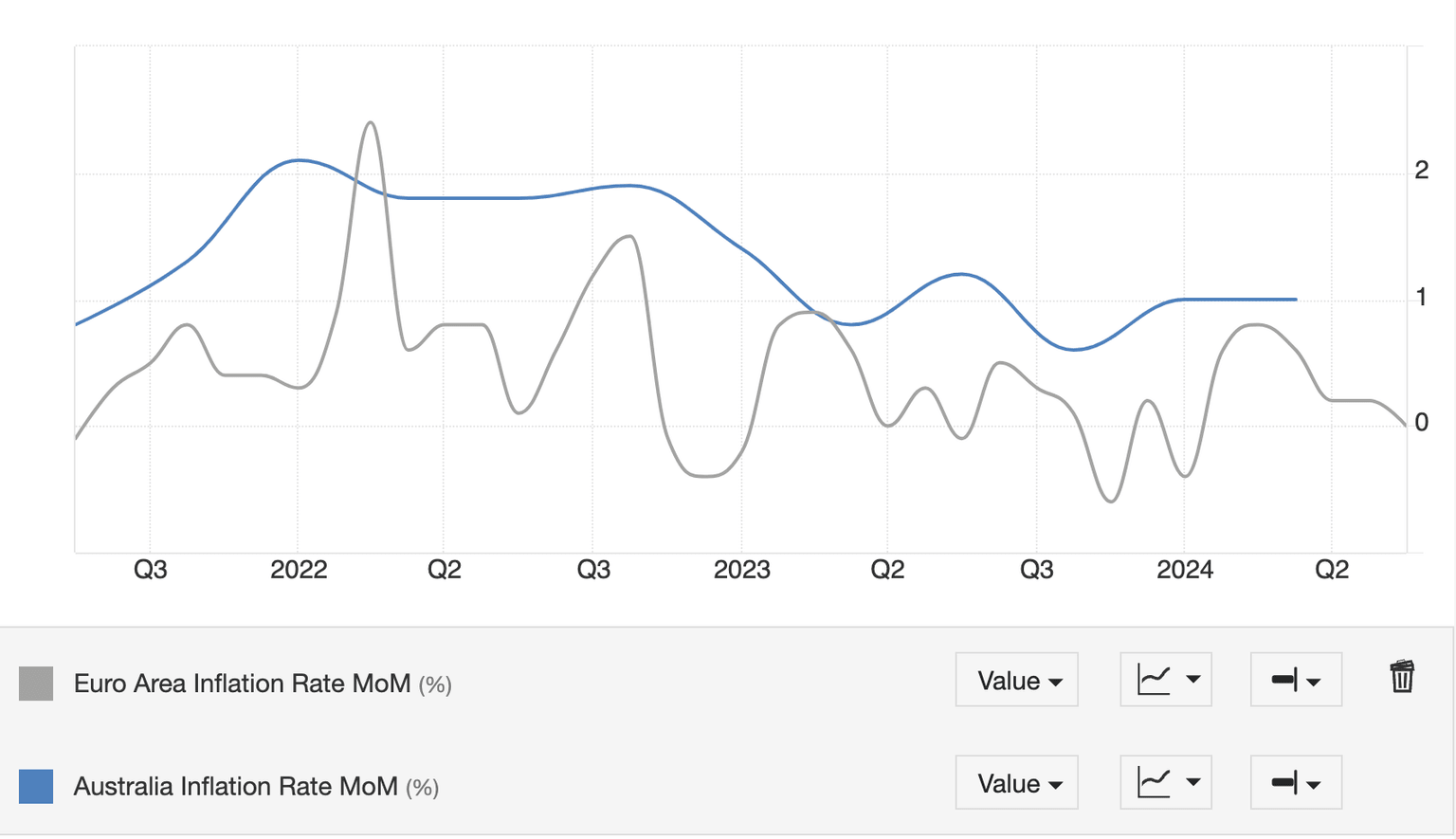
This is most clearly seen in a comparison of the inflation rate on a month-over-month basis, which shows Australian inflation recovering at the same time as Eurozone inflation has fallen to zero.
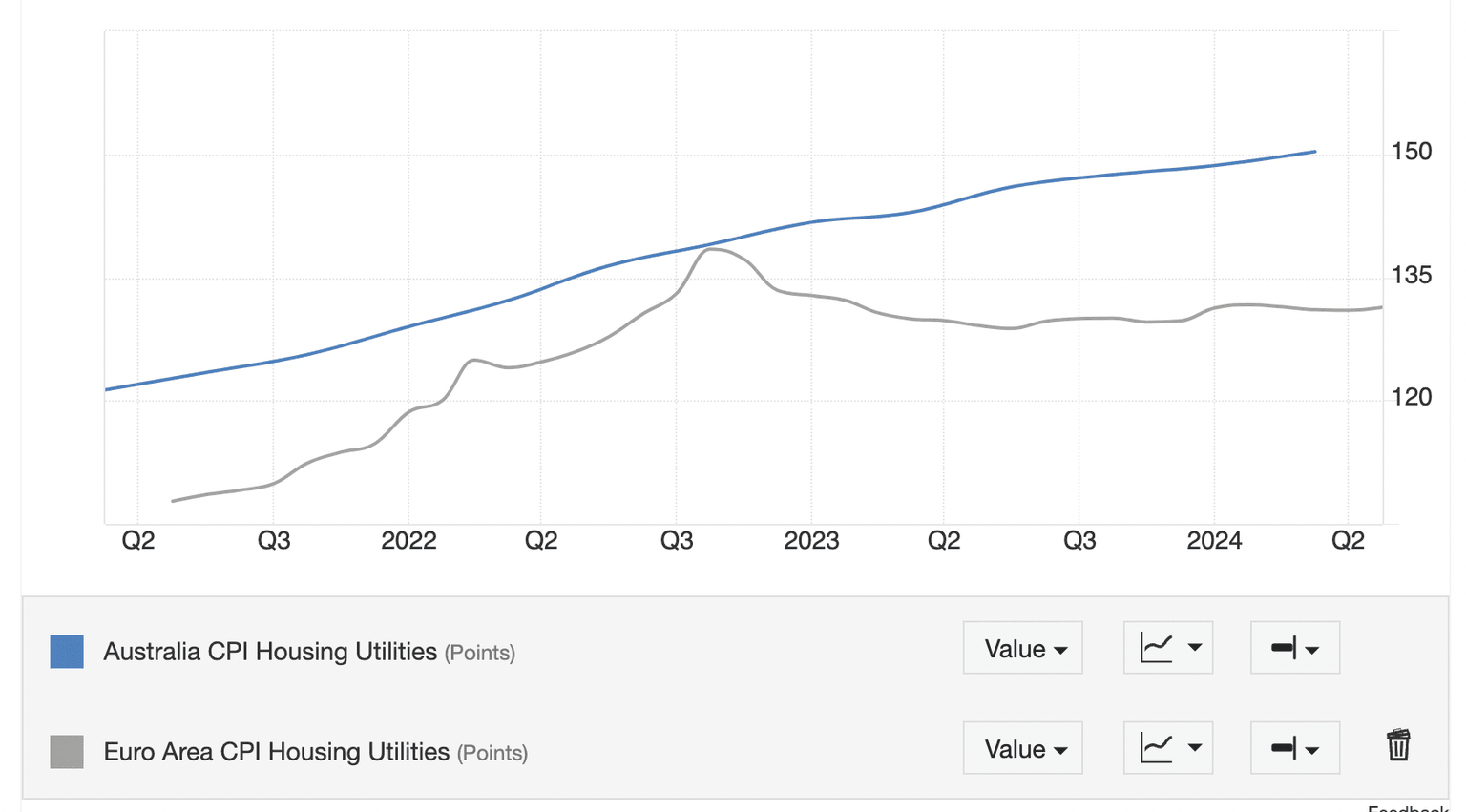
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) for Housing and Utilities is another metric that is showing a wide divergence between the Eurozone and Australia. In the former, the metric began falling in Q3 of 2022 whilst in Australia it continues to rise.
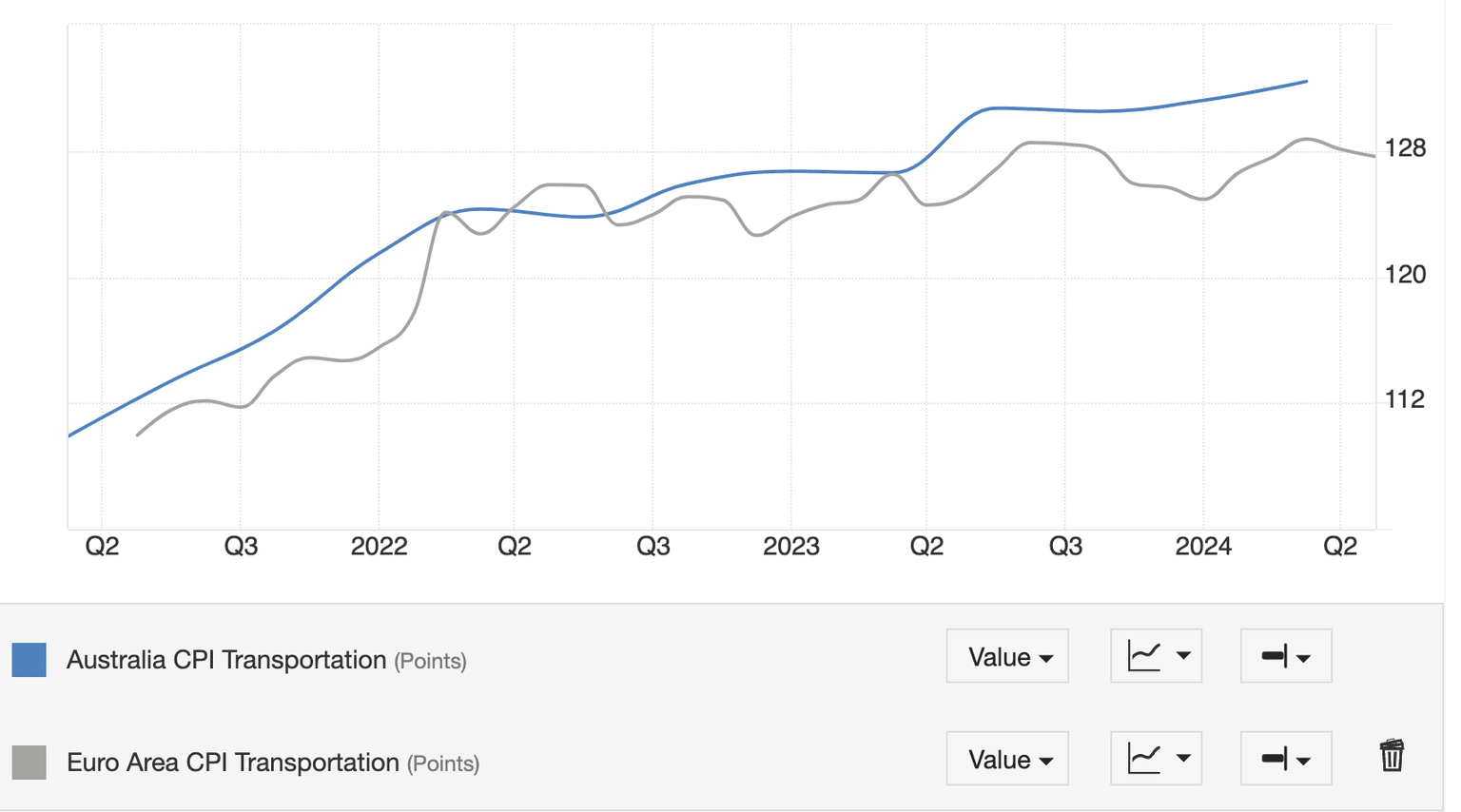
Australian Transportation CPI continues to steadily rise whilst it is plateauing in the Eurozone.
A difference in sentiment
Recent sentiment data has also highlighted a divergence between the two economies. In Australia recent economic sentiment data in the form of the NAB Business Sentiment index and the Westpac-Melbourne Consumer Sentiment Index showed families and businesses remained relatively optimistic about the outlook.
The Westpac-Melbourne index showed that the “family finances vs a year ago” sub-index surged 11.7% to a two-year top of 70.9. The NAB confidence data showed an improvement in the employment situation.
“We were concerned about the sharp decline in the employment index, but it jumped back to an above-average level this month, suggesting the robust jobs growth is continuing for now," said NAB Chief Economist Alan Oster.
The German ZEW Economic Sentiment indicator, conversely, showed the opposite – that sentiment was “breaking down”.
The headline German ZEW Index dropped sharply to 19.2 in August from 41.8 in July, and missed the market consensus of 38.0.
The Current Situation Index worsened from -68.9 in July to -77.3 in the eighth month of the year.
The Eurozone ZEW Economic Sentiment Index came in at 17.9 in August, sharply lower than the July reading of 43.7. The data fell short of the market expectation of 35.4.
Overall the much worsening sentiment in the Eurozone compared to Australia is another bearish factor for EUR/AUD.
Australian outlook according to ANZ bank
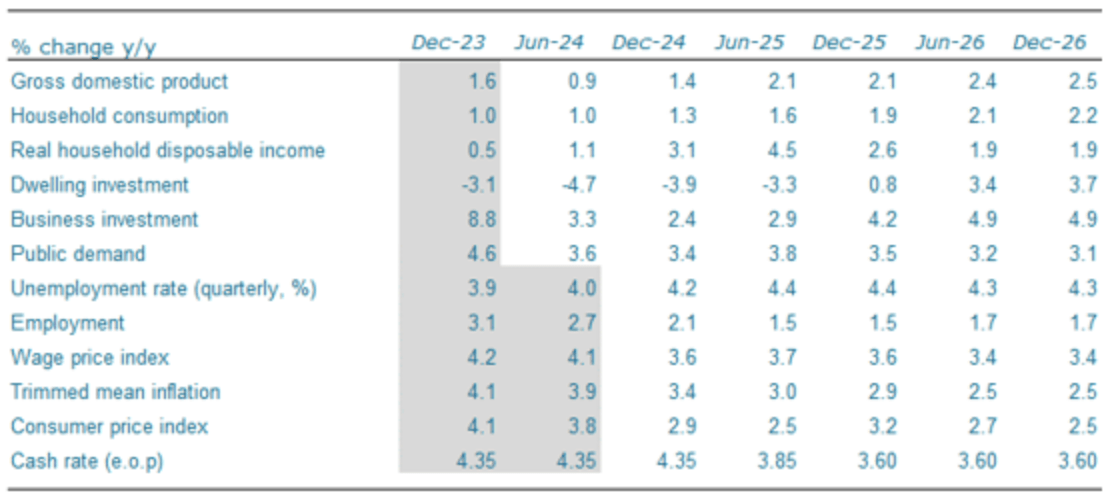
The overall positive outlook for the Australian economy has led ANZ bank, a major New Zealand lender to revise up most of its forecasts for key macroeconomic indicators in Australia.
“Our broad outlook remains that real household disposable incomes will get a significant boost from tax cuts and cost‑of‑living relief measures from H2 2024,” says Adam Boyton, Economist for ANZ.
A rise in consumer spending, business investment and GDP along with a fall in population growth should boost GDP and consumption per capita, says the bank.
Despite foreseeing marginally higher unemployment, ANZ also sees the Wage Price Index (WPI) remaining elevated, in part due to “the announced 15% wage increase for childcare workers”.
Regarding inflation, ANZ expects headline inflation to slow sharply in Q3 to 2.7% YoY, reflecting the temporary effects of cost-of-living relief measures. But it is likely to rebound to above 3.0% in H2 2025.
ANZ expects the RBA to begin cutting rates in February 2025 with the cash rate to end 2025 at 3.60%.
Author

Joaquin Monfort
FXStreet
Joaquin Monfort is a financial writer and analyst with over 10 years experience writing about financial markets and alt data. He holds a degree in Anthropology from London University and a Diploma in Technical analysis.