In last week’s article, which you can read here, I wrote about an example of selling Put options to take advantage of what seemed to be high volatility. At the end of that article, I said that a short put position could be hedged to change its risk profile, Today we’ll explore that further.
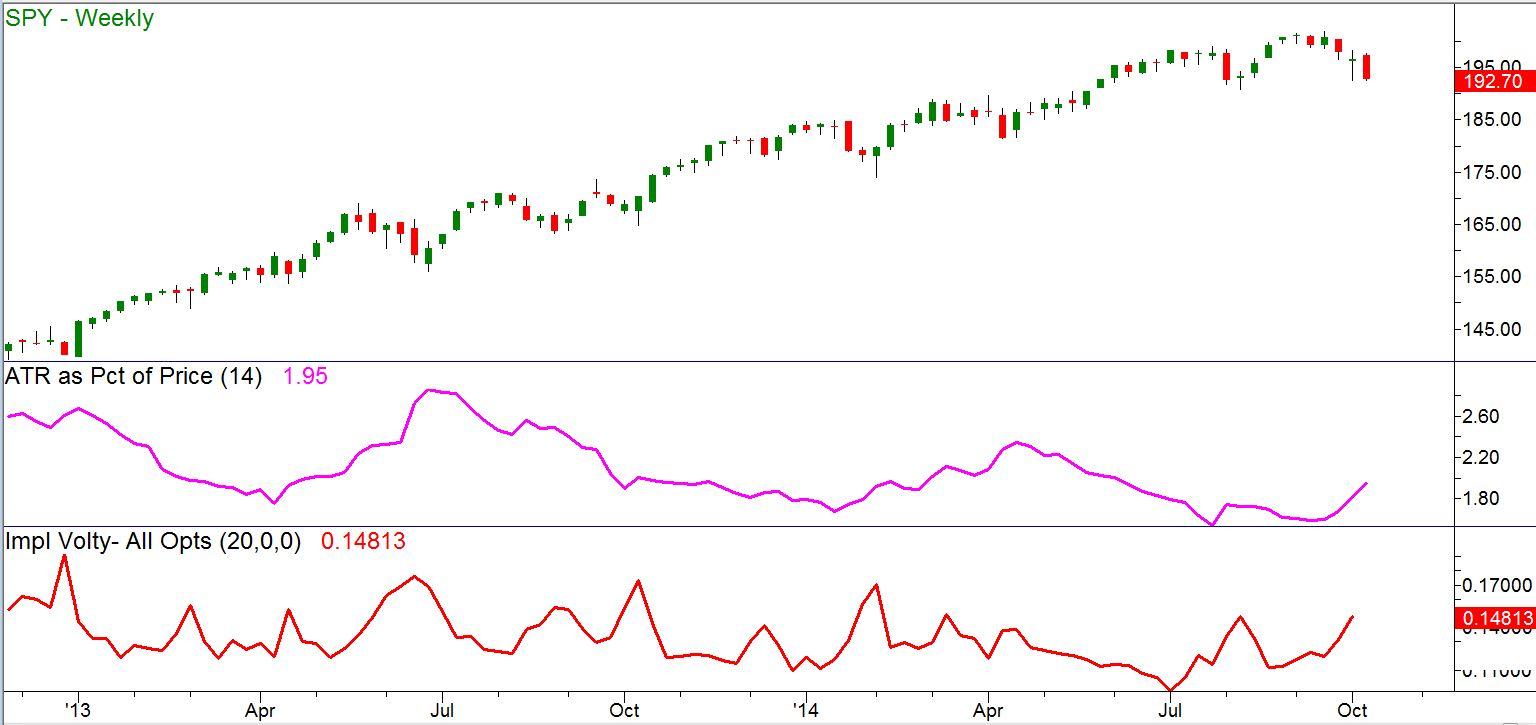
In that example, we looked at selling October put options at the $186 strike price with 8 days to go, for $50 per contract. Here is the price chart as it looked at the time the article was written:
Figure 1 – SPY weekly price chart as of October 9, 2014
The reasons for considering the short 186 puts were:
Implied Volatility (IV), representing the “inflatedness” of options, was higher than it had been for most of 2014, at a reading of 14.8%. This meant that the amount we could be collect for selling options short was relatively
A swing low around $186 from early August looked as though it could very well hold for the few days until expiration.
If SPY did go below $186 we would be forced to buy it at that price; subtracting our $.50 per share proceeds from the put sale, our net cost would be $185.50. With the chart as it appeared then, this was a price that we would not have minded paying.
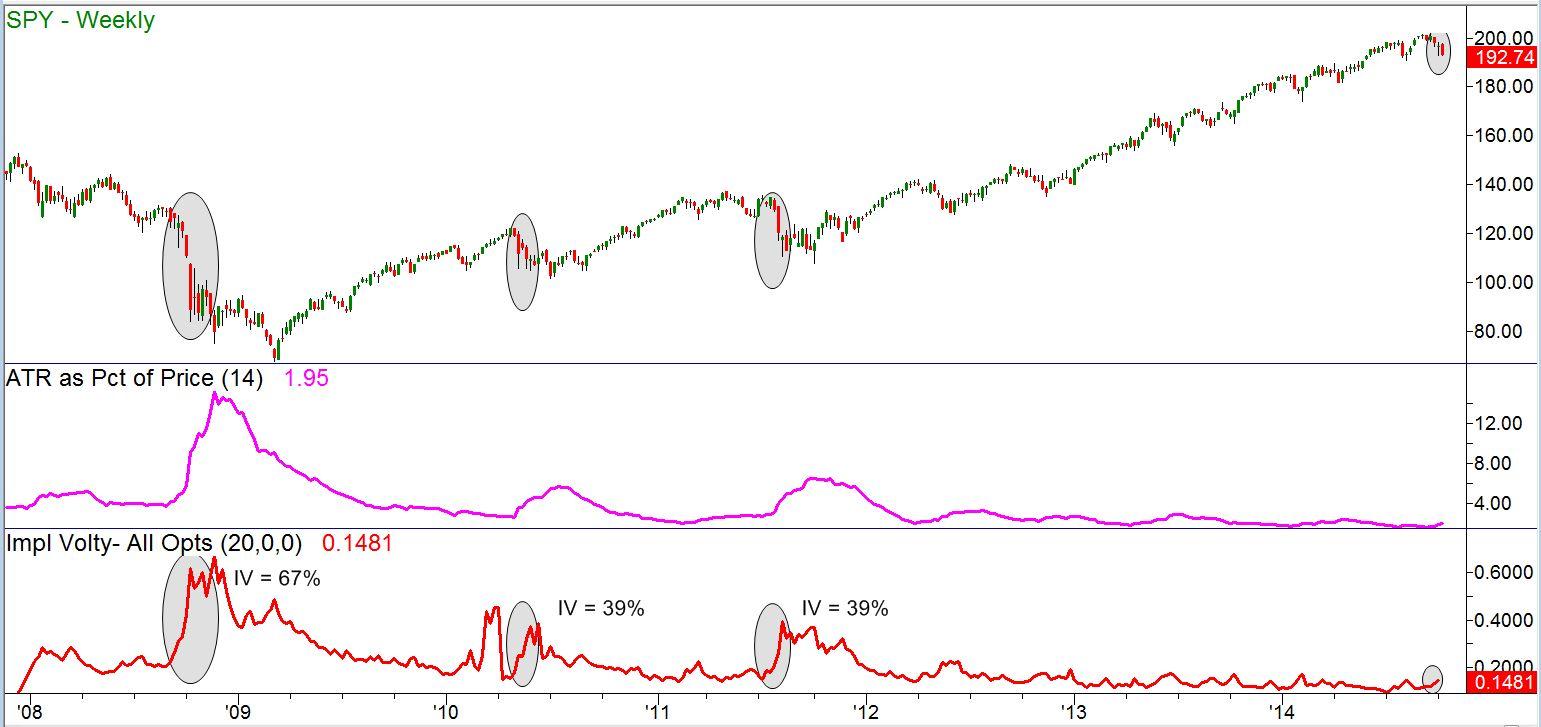
Note that I warned at the time that this was not a recommendation – just an example of how one might consider taking advantage of inflated option prices. I also showed a longer-term chart for perspective, reproduced here:
Figure 2 – SPY weekly price chart, 2008-2014
I noted that “the current IV reading of 15%, while pretty high for the last year, is nowhere near the levels that occurred in previous major drops in 2011 when it reached 39% in 2010 and worst of all in 2008 (67%)… So it’s clear here that a ‘high’ reading of IV now doesn’t necessarily mean that IV can’t go even higher.”
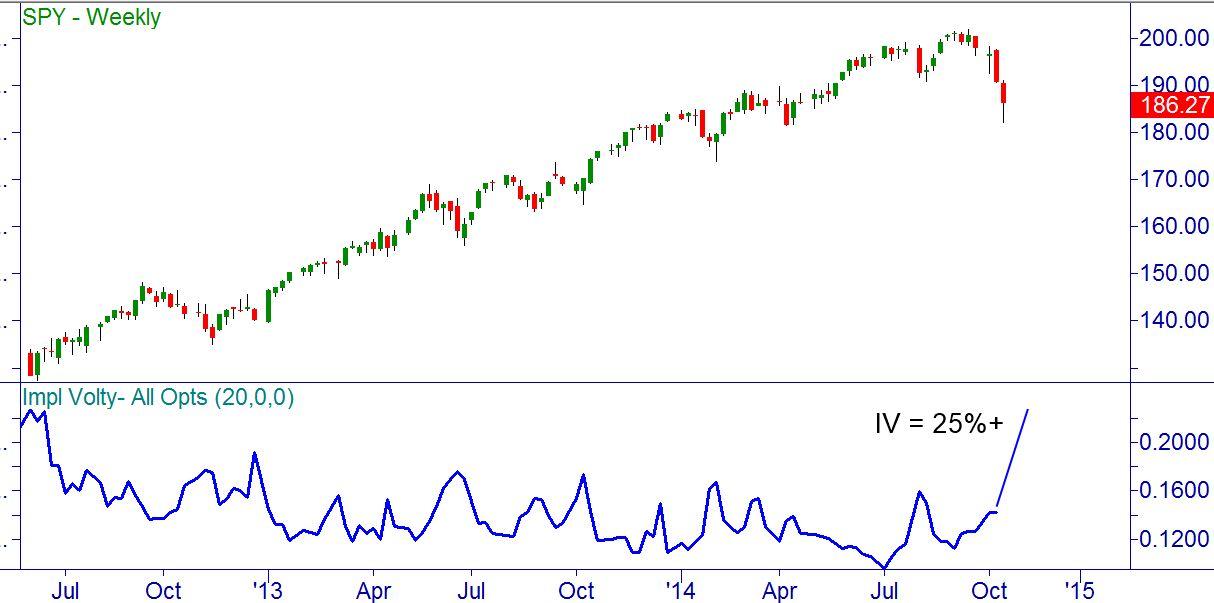
As it has developed, SPY dropped a huge amount and IV did in fact go quite a bit higher:
Figure 3 – SPY weekly chart as of October 16, 2014
At the close on October 16, the day before expiration, SPY was at $186.27, and IV had gone from 14% to over 25%. This meant that option traders on average now believed that SPY could move in a range that was 25% wide, or plus or minus 46 points. The 15% IV reading that had seemed high the week before had now been exceeded by a long shot.
Traders had good reason to believe in increased movement going forward. On Wednesday SPY had traded in an extreme range from $187.69 all the way down to $181.92, closing that day at $186.42.
As of Thursday, the 186 short put was now in danger of being assigned. That would happen if SPY closed even twenty-seven cents lower the next day, which was expiration day. In that case, after the Friday close we would be forced to buy SPY at $186 per share. We would have a loss to the extent, if any, that SPY was below our net cost on the following Monday morning. That net cost would be the $186 that would be extracted from our account to pay for the SPY, less the $.50 that we earlier received for selling the 186 put, or $185.50. Since SPY had gone as low as $181.92 on Wednesday, owning it at $185.50 was a little scary.
So the question was – should we maintain the short 186 put position through expiration, or buy it back?
In favor of buying back the short put:
SPY might be much lower than our $185.50 net cost on Monday, we would then have a loss.
The size of that possible loss was virtually unlimited.
In favor of maintaining the position:
SPY was still above the $186 strike price, and might remain so, giving us our $.50 profit.
Since the next day was expiration day, with a large net put open interest balance, there would be upward pressure on SPY. (Option market makers sell stock, as a hedge, when they sell puts. When the hedge is no longer needed, they buy the stock back. The opposite happens with call options. If there are many more open put options than call options as expiration approaches, more stock must be bought than sold by option market makers collectively. This would add buying pressure which could help push the stock up).
Implied volatility was now much higher than when we sold the put. Buying it back now would guarantee a sizable loss. The 186 put, for which we had received $.50 on October 9, had traded at prices from $.49 to $4.82 in the last two days, and opened on Thursday at $3.66.
The price chart was ambiguous. Although SPY had broken the level around $185 that we saw as our support when we sold the puts, it had been just a brief wick down before snapping back up. Another demand level was below at around $181.
Under these circumstances, a trader might very well have decided to take loss before it got any worse, and bail on the short puts. This could have been done by buying them back on Thursday, on which they traded between $.68 and $3.83. (!)
If the trader had had a crystal ball, and had been able to see that SPY would open on Friday with a large gap up and trade higher, closing at $188.47 and leaving the $186 puts to expire worthless as planned, he could have left those short puts on and slept soundly.
We of course do not have a crystal ball. However, we could have taken steps that could also have let us sleep better. I mentioned last week that a seller of put options can reduce his risk by “hedging” the position.
There are many ways to hedge a position. The most straightforward of these is simply to buy an option of the same type as the one you sold, at a different strike price, so that the second, “insurance” put pays off if the “moneymaker,” or anchor put goes bad.
In this case, at the time we sold the Oct 186 puts at $.50, we could have bought the Oct 181 puts for $.16. This sixteen cents for insurance reduced our maximum net profit by that amount. But it also changed our maximum loss from “unlimited” to a finite amount of less than five dollars per share. In the best case, if SPY closed on expiration day above $186, both puts would expire worthless. We would be left with the $.34 per share difference between the fifty cents we received for the 186 moneymaker puts, and the sixteen cents we paid for the 181 insurance puts.
If the worst happened, and SPY were to end on Friday much lower than 186, our loss would now be limited. If it were to close at expiration day at 180, for example:
The SPY would be “put to” us, meaning we would receive it, and have to pay $186 per share, as the 186 puts were exercised and we were assigned to fulfill our obligation.
We would in turn exercise our 181 puts and “put the stock back”, receiving $181 per share.
Our net loss would be $186 – $181, or $5.00, less the $.34 net credit we earlier received (receiving $.50 for the 186 puts and paying $.16 for the 181 puts). The net loss would thus be $5.00 – $.34 = $4.66.
This is the maximum net loss we could have, no matter how low the price of SPY should go, even to zero.
Our “return on risk” for this trade would be $.34 / $4.66, or about 7% in 8 days.
If a trader had chosen to hedge the unlimited risk of the short puts, by buying insurance puts as described above, he might have had the confidence to hold on to what turned out to be a winning position. This illustrates one of the virtues of hedging. It can help you to stay in a position when that makes logical sense, knowing that the worst-case result is known and tolerable.
Note that I am stretching a point here by saying that staying in this particular trade would have made logical sense. A good case can be made against that. But I hope you can see my main point, which is that our decision on whether to go or stay in a trade is a different calculation when our worst-case scenario is not a catastrophe. This can make the difference between being able to ride out a trade that turns into a winner, or “panicking out” too soon.
I’ll have a lot more to say about hedging in future articles.
This content is intended to provide educational information only. This information should not be construed as individual or customized legal, tax, financial or investment services. As each individual's situation is unique, a qualified professional should be consulted before making legal, tax, financial and investment decisions. The educational information provided in this article does not comprise any course or a part of any course that may be used as an educational credit for any certification purpose and will not prepare any User to be accredited for any licenses in any industry and will not prepare any User to get a job. Reproduced by permission from OTAcademy.com click here for Terms of Use: https://www.otacademy.com/about/terms
Editors’ Picks

EUR/USD: US Dollar to remain pressured until uncertainty fog dissipates Premium
The EUR/USD pair lost additional ground in the first week of February, settling at around 1.1820. The reversal lost momentum after the pair peaked at 1.2082 in January, its highest since mid-2021.

Gold: Volatility persists in commodity space Premium
After losing more than 8% to end the previous week, Gold (XAU/USD) remained under heavy selling pressure on Monday and dropped toward $4,400. Although XAU/USD staged a decisive rebound afterward, it failed to stabilize above $5,000.

GBP/USD: Pound Sterling tests key support ahead of a big week Premium
The Pound Sterling (GBP) changed course against the US Dollar (USD), with GBP/USD giving up nearly 200 pips in a dramatic correction.

Bitcoin: The worst may be behind us
Bitcoin (BTC) price recovers slightly, trading at $65,000 at the time of writing on Friday, after reaching a low of $60,000 during the early Asian trading session. The Crypto King remained under pressure so far this week, posting three consecutive weeks of losses exceeding 30%.

Three scenarios for Japanese Yen ahead of snap election Premium
The latest polls point to a dominant win for the ruling bloc at the upcoming Japanese snap election. The larger Sanae Takaichi’s mandate, the more investors fear faster implementation of tax cuts and spending plans.
RECOMMENDED LESSONS
Making money in forex is easy if you know how the bankers trade!
I’m often mystified in my educational forex articles why so many traders struggle to make consistent money out of forex trading. The answer has more to do with what they don’t know than what they do know. After working in investment banks for 20 years many of which were as a Chief trader its second knowledge how to extract cash out of the market.
5 Forex News Events You Need To Know
In the fast moving world of currency markets where huge moves can seemingly come from nowhere, it is extremely important for new traders to learn about the various economic indicators and forex news events and releases that shape the markets. Indeed, quickly getting a handle on which data to look out for, what it means, and how to trade it can see new traders quickly become far more profitable and sets up the road to long term success.
Top 10 Chart Patterns Every Trader Should Know
Chart patterns are one of the most effective trading tools for a trader. They are pure price-action, and form on the basis of underlying buying and selling pressure. Chart patterns have a proven track-record, and traders use them to identify continuation or reversal signals, to open positions and identify price targets.
7 Ways to Avoid Forex Scams
The forex industry is recently seeing more and more scams. Here are 7 ways to avoid losing your money in such scams: Forex scams are becoming frequent. Michael Greenberg reports on luxurious expenses, including a submarine bought from the money taken from forex traders. Here’s another report of a forex fraud. So, how can we avoid falling in such forex scams?
What Are the 10 Fatal Mistakes Traders Make
Trading is exciting. Trading is hard. Trading is extremely hard. Some say that it takes more than 10,000 hours to master. Others believe that trading is the way to quick riches. They might be both wrong. What is important to know that no matter how experienced you are, mistakes will be part of the trading process.
The challenge: Timing the market and trader psychology
Successful trading often comes down to timing – entering and exiting trades at the right moments. Yet timing the market is notoriously difficult, largely because human psychology can derail even the best plans. Two powerful emotions in particular – fear and greed – tend to drive trading decisions off course.