EUR/USD Forecast: Euro corrective losses to remain limited in near term
- EUR/USD stays in a consolidation phase at around 1.1500 on Tuesday.
- Markets could refrain from betting on a steady recovery in the US Dollar.
- The pair's near-term technical outlook suggests that the bullish bias remains intact.

EUR/USD seems to have entered a consolidation phase near 1.1500 after gaining more than 1% and touching its highest level since 2021 above 1.1570. The pair's technical outlook suggests that the bullish bias remains intact in the near term, while signalling a loss of momentum.
Euro PRICE This week
The table below shows the percentage change of Euro (EUR) against listed major currencies this week. Euro was the strongest against the US Dollar.
| USD | EUR | GBP | JPY | CAD | AUD | NZD | CHF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USD | -0.92% | -0.62% | -1.18% | -0.22% | -0.45% | -1.27% | -0.78% | |
| EUR | 0.92% | 0.15% | -0.27% | 0.67% | 0.29% | -0.38% | 0.11% | |
| GBP | 0.62% | -0.15% | -0.24% | 0.53% | 0.14% | -0.52% | -0.03% | |
| JPY | 1.18% | 0.27% | 0.24% | 0.97% | 0.60% | 0.02% | 0.43% | |
| CAD | 0.22% | -0.67% | -0.53% | -0.97% | -0.36% | -1.04% | -0.55% | |
| AUD | 0.45% | -0.29% | -0.14% | -0.60% | 0.36% | -0.65% | -0.17% | |
| NZD | 1.27% | 0.38% | 0.52% | -0.02% | 1.04% | 0.65% | 0.51% | |
| CHF | 0.78% | -0.11% | 0.03% | -0.43% | 0.55% | 0.17% | -0.51% |
The heat map shows percentage changes of major currencies against each other. The base currency is picked from the left column, while the quote currency is picked from the top row. For example, if you pick the Euro from the left column and move along the horizontal line to the US Dollar, the percentage change displayed in the box will represent EUR (base)/USD (quote).
The US Dollar (USD) came under heavy selling pressure at the beginning of the week on growing fears over the Federal Reserve (Fed) losing its independence. The USD Index dropped to its weakest level in three years and lost about 1% on Monday.
After White House economic adviser Kevin Hassett said ahead of the weekend that President Donald Trump and his team were continuing to study if firing Fed Chairman Jerome Powell was an option in a way that it wasn't before, Trump took to social media to criticize the Fed's monetary policy decisions on Monday.
Trump argued that there was "virtually no inflation" in the US and that there could be a slowing of the economy unless the Fed were to lower interest rates. He also called Powell "Mr. Too late" and accused him of cutting rates in late 2024 for political reasons.
The economic calendar will not feature any high-tier data releases. Investors will pay close attention to comments from Fed policymakers later in the day. In case officials push back against Trump's criticism and reassure markets that they will not be influenced by politics when setting the policy, investors could breathe a sigh of relief and help the USD recover. On the other hand, markets could remain on edge and make it difficult for the USD to find demand in case Trump doubles down on his intensions of firing Powell.
EUR/USD Technical Analysis
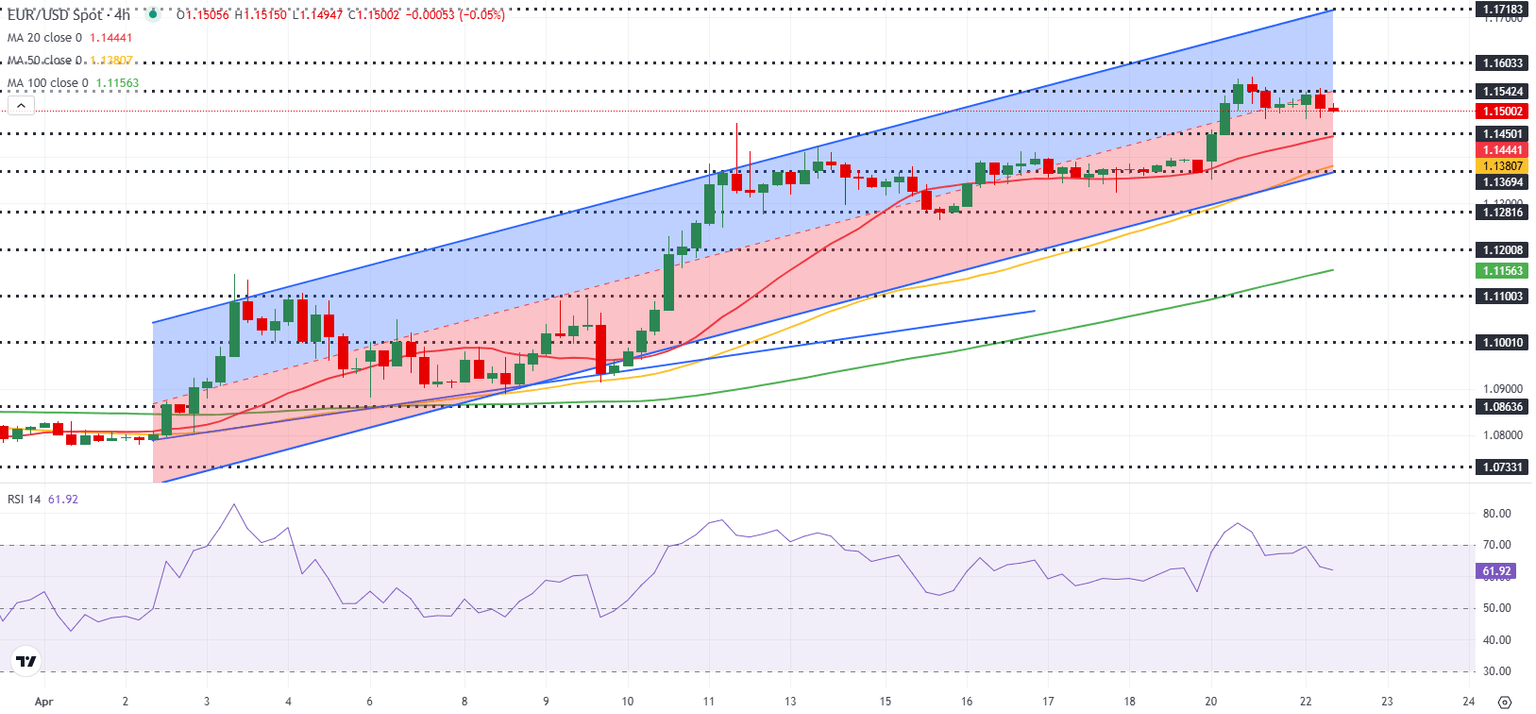
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) indicator on the 4-hour chart retreats toward 60, highlighting that the bullish bias remains intact but loses momentum.
On the downside, 1.1450 (20-period Simple Moving Average (SMA), static level) aligns as first support level before 1.1380 (50-period SMA, lower limit of the ascending channel) and 1.1300 (static level, round level). Looking north, resistances could be located at 1.1540 (mid-point of the ascending channel), 1.1600 (static level, round level) and 1.1720 (upper limit of the ascending channel).
Fed FAQs
Monetary policy in the US is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these goals is by adjusting interest rates. When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% target, it raises interest rates, increasing borrowing costs throughout the economy. This results in a stronger US Dollar (USD) as it makes the US a more attractive place for international investors to park their money. When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates to encourage borrowing, which weighs on the Greenback.
The Federal Reserve (Fed) holds eight policy meetings a year, where the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) assesses economic conditions and makes monetary policy decisions. The FOMC is attended by twelve Fed officials – the seven members of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the remaining eleven regional Reserve Bank presidents, who serve one-year terms on a rotating basis.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve may resort to a policy named Quantitative Easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is a non-standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy high grade bonds from financial institutions. QE usually weakens the US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process of QE, whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing, to purchase new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US Dollar.
Premium
You have reached your limit of 3 free articles for this month.
Start your subscription and get access to all our original articles.
Author

Eren Sengezer
FXStreet
As an economist at heart, Eren Sengezer specializes in the assessment of the short-term and long-term impacts of macroeconomic data, central bank policies and political developments on financial assets.

















