EUR/USD weakens as PPI beat hits Fed policy expectations
- EUR/USD down 0.57% to 1.1638 after US PPI and Core PPI surged in July.
- Tariff pass-through fuels inflation while jobless claims dip, signaling labor market resilience.
- Market erases 50 bps September Fed cut bets, some pricing in chance of no cut.

EUR/USD dives sharply on Thursday as the latest inflation report in the United States (US) caught traders off guard, who were betting on a slim chance of a 50 basis points (bps) Federal Reserve (Fed) rate cut in September. Currently, the pair trades at 1.1638, down 0.57%.
The US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) revealed that the Producer Price Index (PPI) in headline and core prints accelerated sharply, mainly influenced by higher tariff levels imposed by the US. Meanwhile, jobs data showed that the number of people filing for unemployment benefits dipped compared to the previous reading, as revealed by the Department of Labor (DoL).
Consequently, market participants had taken off the table the possibility of a jumbo rate cut. Instead, they’re pricing in a slim chance that the Fed might hold rates unchanged at the September 16-17 meeting.
After the data, some Fed officials crossed the wires. St. Louis Fed President Alberto Musalem said that inflation is running close to 3%, adding that tariffs are feeding through inflation. The Richmond Fed President Thomas Barkin said that business sentiment had picked up, but not in terms of hiring.
In the Eurozone, Gross Domestic Product (GDP) figures came in as expected, though Industrial Production tanked in June, influenced by a dip in Germany and weak consumer goods production.
Despite the ongoing weakness shown in today’s data, further EUR/USD upside is seen. The Fed is expected to cut rates in September, while most economists expect the European Central Bank (ECB) to keep rates unchanged. The reduction of the interest rate differential between the US and the bloc would strengthen the Euro.
On Friday, the European Union (EU) economic docket will be absent. In the US, the schedule will feature Retail Sales, Industrial Production, and the University of Michigan (UoM) Consumer Sentiment index.
Euro PRICE This week
The table below shows the percentage change of Euro (EUR) against listed major currencies this week. Euro was the strongest against the New Zealand Dollar.
| USD | EUR | GBP | JPY | CAD | AUD | NZD | CHF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USD | -0.02% | -0.65% | 0.16% | 0.41% | 0.39% | 0.65% | -0.16% | |
| EUR | 0.02% | -0.64% | 0.19% | 0.44% | 0.43% | 0.62% | -0.13% | |
| GBP | 0.65% | 0.64% | 0.78% | 1.07% | 1.05% | 1.27% | 0.51% | |
| JPY | -0.16% | -0.19% | -0.78% | 0.27% | 0.27% | 0.57% | -0.17% | |
| CAD | -0.41% | -0.44% | -1.07% | -0.27% | 0.00% | 0.19% | -0.58% | |
| AUD | -0.39% | -0.43% | -1.05% | -0.27% | -0.01% | 0.21% | -0.54% | |
| NZD | -0.65% | -0.62% | -1.27% | -0.57% | -0.19% | -0.21% | -0.75% | |
| CHF | 0.16% | 0.13% | -0.51% | 0.17% | 0.58% | 0.54% | 0.75% |
The heat map shows percentage changes of major currencies against each other. The base currency is picked from the left column, while the quote currency is picked from the top row. For example, if you pick the Euro from the left column and move along the horizontal line to the US Dollar, the percentage change displayed in the box will represent EUR (base)/USD (quote).
Daily digest market movers: The Euro is weighed by hot PPI print
- EUR/USD tumbles following the latest jobs and inflation reports in the US. Initial Jobless Claims fell to 224,000 for the week ending August 9, beating expectations of 228,000 and down from 227,000 the prior week. Continuing Claims fell to 1.953 million from 1.968 million, easing concerns over a significant cooling in the labor market.
- Factory gate inflation, officially known as the PPI, soared by 0.9% MoM in July, bouncing off a flat reading in June. In the twelve months to July, the PPI accelerated to 3.3% from 2.4%, well above the 2.5% forecast. Core PPI—which feeds into the Fed’s preferred inflation measure, the Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) Price Index—soared 3.7% YoY, well above June’s 2.6% print, a sign that businesses are passing tariff-related cost pressures on to consumers.
- Across the pond, the Eurozone Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in Q2 rose by 1.4% YoY as expected, unchanged from the previous reading. The quarterly figure aligned with forecasts at 0.1%, unchanged from the prior print. Other data showed that Eurozone Industrial Production dipped sharply, -1.3% MoM in June, from May’s 1.7% expansion.
- The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the performance of the buck’s value against a basket of its peers, rallies some 0.42% at 98.19, a headwind for EUR/USD.
- The latest economic data released in the US spurred investors' speculation that the Federal Reserve might resume its easing cycle at the upcoming September meeting. Odds for a quarter of a percentage cut are at 92%, revealed Prime Market Terminal (PMT).
- On the European Central Bank (ECB) front, the easing cycle seems to be on pause for the September meeting, with 90% odds for the ECB to keep rates unchanged, and a slim 10% chance of a 25 basis points (bps) rate cut.
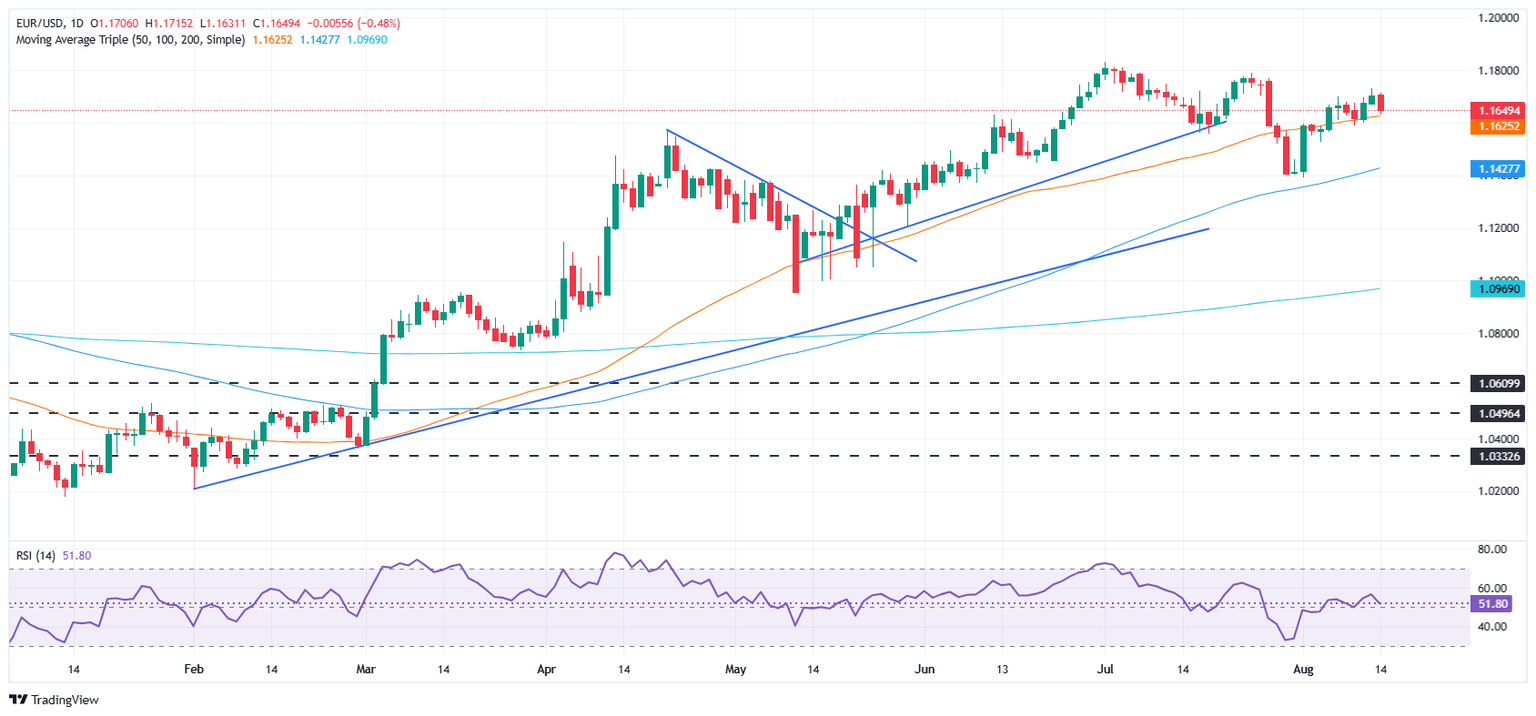
Technical outlook: EUR/USD retreats below 1.1650 as sellers target 1.1500
The EUR/USD uptrend remains intact, even though the pair dipped toward the confluence of the 20- and 50-day Simple Moving Averages (SMAs) at around 1.1624/30. Nevertheless, a daily close below the latter can prompt traders to challenge 1.1600 in the near term. If cleared, the next area of demand would be 1.1500.
Instead, if EUR/USD climbs back above 1.1650, a move towards 1.1700 is on the cards. A breach of the latter will expose the current week’s high at 1.1730, 1.1759, and the year-to-date (YTD) high at 1.1829.
ECB FAQs
The European Central Bank (ECB) in Frankfurt, Germany, is the reserve bank for the Eurozone. The ECB sets interest rates and manages monetary policy for the region. The ECB primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which means keeping inflation at around 2%. Its primary tool for achieving this is by raising or lowering interest rates. Relatively high interest rates will usually result in a stronger Euro and vice versa. The ECB Governing Council makes monetary policy decisions at meetings held eight times a year. Decisions are made by heads of the Eurozone national banks and six permanent members, including the President of the ECB, Christine Lagarde.
In extreme situations, the European Central Bank can enact a policy tool called Quantitative Easing. QE is the process by which the ECB prints Euros and uses them to buy assets – usually government or corporate bonds – from banks and other financial institutions. QE usually results in a weaker Euro. QE is a last resort when simply lowering interest rates is unlikely to achieve the objective of price stability. The ECB used it during the Great Financial Crisis in 2009-11, in 2015 when inflation remained stubbornly low, as well as during the covid pandemic.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse of QE. It is undertaken after QE when an economic recovery is underway and inflation starts rising. Whilst in QE the European Central Bank (ECB) purchases government and corporate bonds from financial institutions to provide them with liquidity, in QT the ECB stops buying more bonds, and stops reinvesting the principal maturing on the bonds it already holds. It is usually positive (or bullish) for the Euro.
Author

Christian Borjon Valencia
FXStreet
Markets analyst, news editor, and trading instructor with over 14 years of experience across FX, commodities, US equity indices, and global macro markets.

















