Will Biden trigger inflation for Gold?

President-elect Joe Biden is expected to increase further government spending. For this and also other reasons, there is a risk that inflation under Biden’s presidency could be higher than under Trump’s. That would be great news for gold.
Let’s face it, Biden won’t have an easy presidency. And I’m not referring to the fact that he will be sworn in as the oldest president in U.S. history or that he will have to deal with the coronavirus pandemic and the process of vaccine distribution across the country. I’m referring to Biden inheriting an economy with slow growth and too much public debt . Given the debt burden, it should be clear that under Biden’s presidency, real interest rates will remain at ultra-low levels. This is how a debt trap works – the more the debt grows, the less the economy (Treasury) can afford higher interest rates .
Moreover, Biden will have to face the risk of inflation . Actually, some analysts say that the new POTUS could contribute to the rise of prices. Is it true? Will we finally see an acceleration in the inflation rate?
So far, consumer inflation has been subdued. As the chart below shows, the CPI overall annual rate has declined from 2.3 percent before the epidemic to 1.2 percent in October.
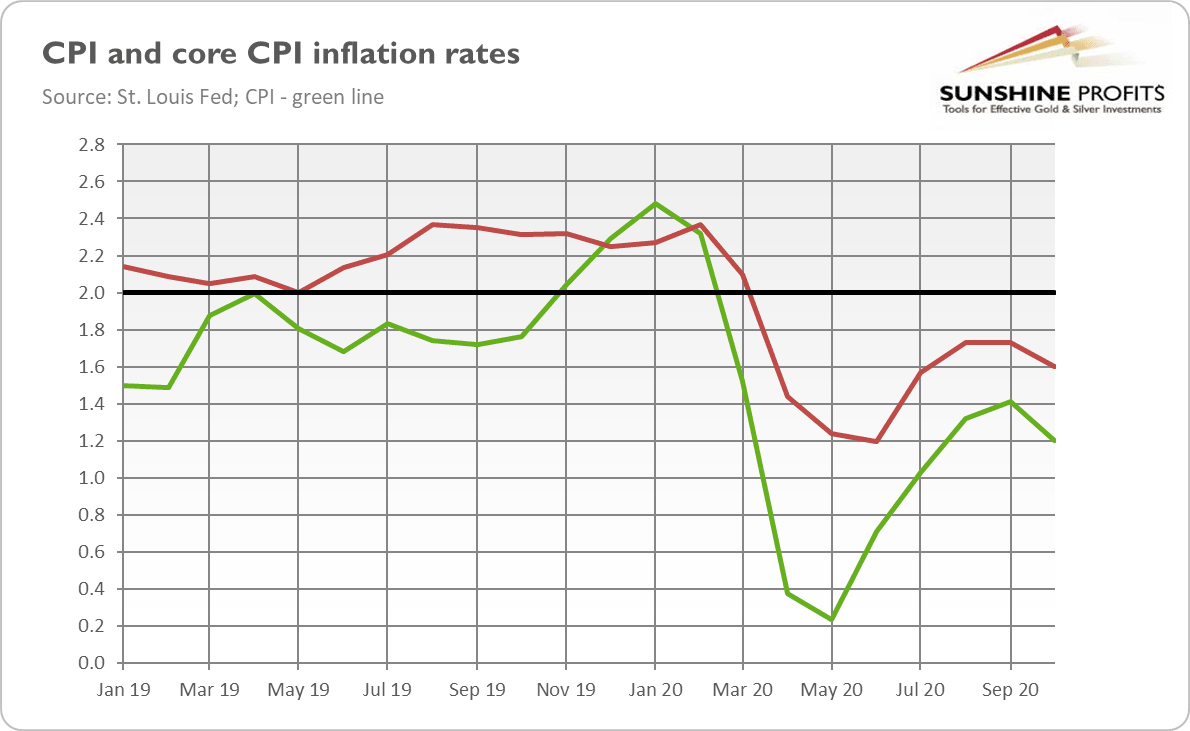
For some people, this is all really surprising given all the money pumped by the Fed into the economy. However, the disinflation is perfectly in line with our predictions from the May edition of the Gold Market Overview : “In the short run, we expect disinflation , but we think that the risk of inflation later in the future is higher than a decade ago.”
Indeed, in the short-run, the negative demand shock outweighed other factors, and people simply increased their demand for money because of the enormous uncertainty and limited opportunities to spend money in the offline economy.
But didn’t the Fed significantly increase the money supply ? It did, but the central banks create only a monetary base , while the majority (more than 90 percent) of the broad money supply is created by the commercial banks. So, for inflationary trends, what really matters is not the Fed’s balance sheet , but rather the commercial banks’ credit expansion, since whenever the banks grant loans, they also create deposits, i.e., money supply.
Hey, wait a moment, but didn’t the pace of expansion of the banks’ credit and broad money supply also rise? They did! Just look at the chart below. And this is the reason why I believe that the risk of inflation in the aftermath of the coronavirus crisis is higher than after the Great Recession , when banks were strongly hit and didn’t want to expand credit.
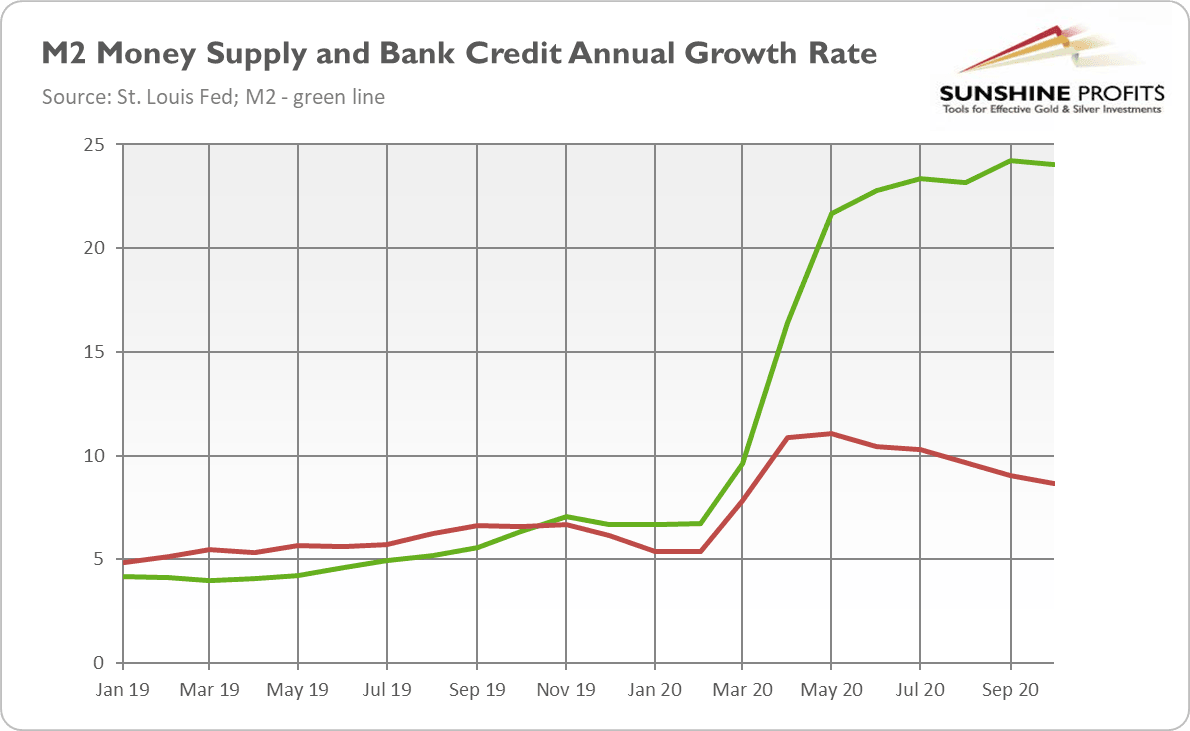
Now the situation is different. However, banks expanded loans not to the consumers but to the entrepreneurs, probably because they needed credit to stay afloat during the Great Lockdown . So, the acceleration in the bank credit could be temporary – indeed, the pace of its expansion has been slowing down recently. But when the pandemic is over, consumers may again tap credit cards and real estate loans.
Indeed, this is an important upward risk for inflation . Some economists point out here the pent-up demand, i.e., the strong increase in demand for a service or product, usually following a period of subdued spending. The idea is that consumers tend to hold off their demand during a recession, only to unleash it during recovery. It makes sense; during a crisis, the uncertainty rises, so people try to cut expenses and accumulate cash. When confidence returns to the marketplace, people spend money more freely.
The same could happen during the current pandemic – not only did uncertainty rise, but people also had to practice social distancing and obey sanitary restrictions, which forced them to reduce their expenditures. Hence, when the pandemic is over, the demand for cash may fall, while spending could increase, thereby accelerating inflation . Of course, some demand will simply stay unrealized forever (it would be impossible to make up for all these missed opportunities to drink beers with friends), but when the storm is over and vaccines boost people’s confidence, they will spend a substantial part of their extra savings accumulated during the pandemic.
Just take a look the chart below – as you can see, the U.S. personal savings rate has increased from about 8 percent before the epidemic to almost 34 percent in April. Now it is staying above 14 percent, so there is still potential to increase consumer spending in the future.
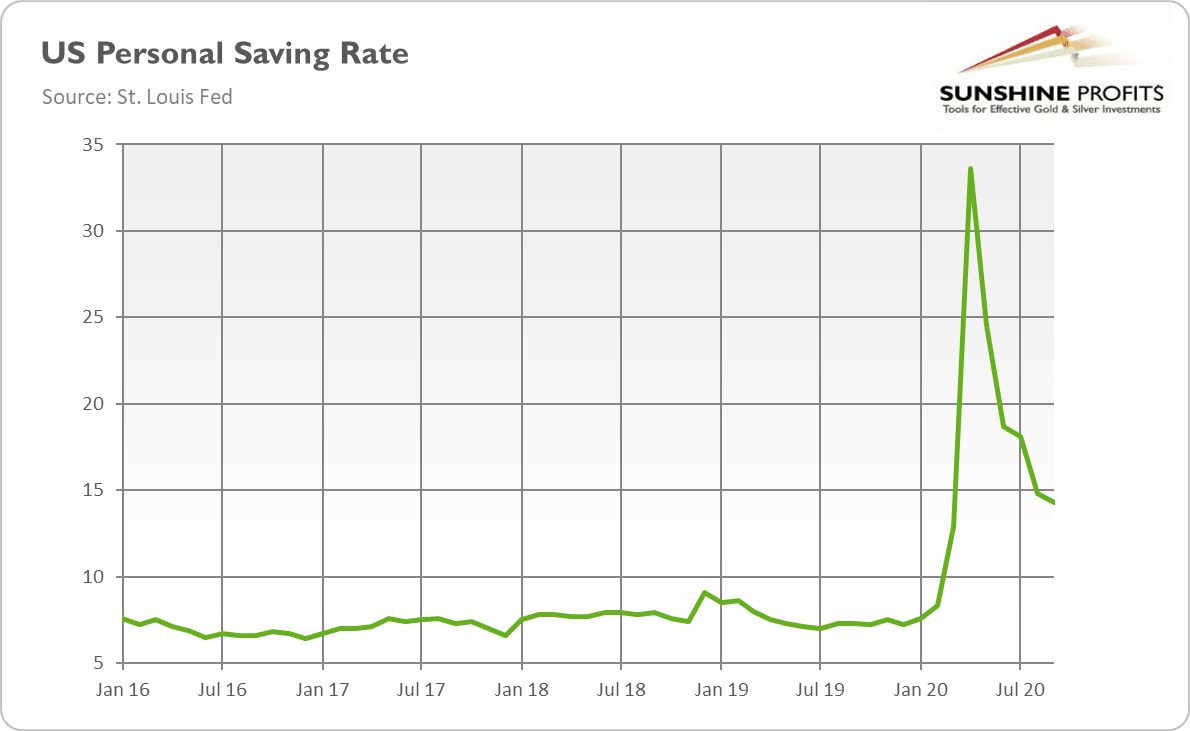
In other words, people and businesses have not yet used all the stimulus they got from the Fed or the government. Because of this uncertainty, they spent as little as they could, and saved as much they could. Why this is so important? Because when people decide to spend their mountain of money, inflation could accelerate, boosting the demand for gold as an inflation hedge .
Hence, when the pandemic storm is over, the demand for money should decrease, or the velocity of money should increase. Actually, this is what we have observed in the third quarter of this year – the velocity of M2 money supply has rebounded somewhat , as the chart below shows. So, although the second wave of COVID-19 infections would hamper this process, it’s possible that in 2021 we will see a rise in inflation. Higher inflation also means lower real interest rates, which is another piece of good news for the yellow metal.

Last but not least, Biden is a supporter of major economic relief, including a second round of stimulus checks, so consumers’ spending power should increase further next year, thus contributing to higher consumer prices. So, although it’s not determined, there is a risk that inflation under Biden’s presidency could be higher than under Trump’s presidency. It would be great news for gold , especially that the Fed’s new regime means that it will not strongly react to rising inflation.
Want free follow-ups to the above article and details not available to 99%+ investors? Sign up to our free newsletter today!
Want free follow-ups to the above article and details not available to 99%+ investors? Sign up to our free newsletter today!
Author

Arkadiusz Sieroń
Sunshine Profits
Arkadiusz Sieroń received his Ph.D. in economics in 2016 (his doctoral thesis was about Cantillon effects), and has been an assistant professor at the Institute of Economic Sciences at the University of Wrocław since 2017.

















