Nixon’s closure of gold window still supports gold prices

August marks the 50th anniversary of Nixon’s closure of the gold window, the end of the gold standard that still affects the global economy.
It’s been 50 years since one of the most important events in contemporary – or, perhaps, all of – economic history. And, no, I don’t mean the foundation of the Nasdaq stock exchange nor the bankruptcy and nationalization of Rolls-Royce. Half a century ago, on August 15, 1971, President Richard Nixon closed the gold window. It meant that America unilaterally canceled the convertibility of the US dollar to gold. Nixon’s action was a nail in the coffin of the Breton Woods system and the beginning of the current monetary system (or, actually, the current non-system) based on freely floating fiat currencies (the ultimate end of the gold standard came in 1973). So, for the first time in history, money ceased to have any intrinsic value, use value, and any links to the precious metals or other commodities. Humankind has begun an experiment with national fiat monies that weren’t in any, even the loosest way, backed by gold.
How did this experiment go then? Not very well… The idea was that unshackling the dollar from gold would allow the Fed to conduct independent and ‘scientific’ monetary policy to boost economic growth and provide full employment while avoiding harmful recessions. Nixon’s shock was also presented as an action that would halt inflation and strengthen the stability of the dollar. As President Nixon promised himself in a television speech on August 15, 1971:
The third indispensable element in building the new prosperity is closely related to creating new jobs and halting inflation. We must protect the position of the American dollar as a pillar of monetary stability around the world (…)
I have directed Secretary Connally to suspend temporarily the convertibility of the dollar into gold or other reserve assets, except in amounts and conditions determined to be in the interest of monetary stability and in the best interests of the United States. (…)
The effect of this action, in other words, will be to stabilize the dollar.
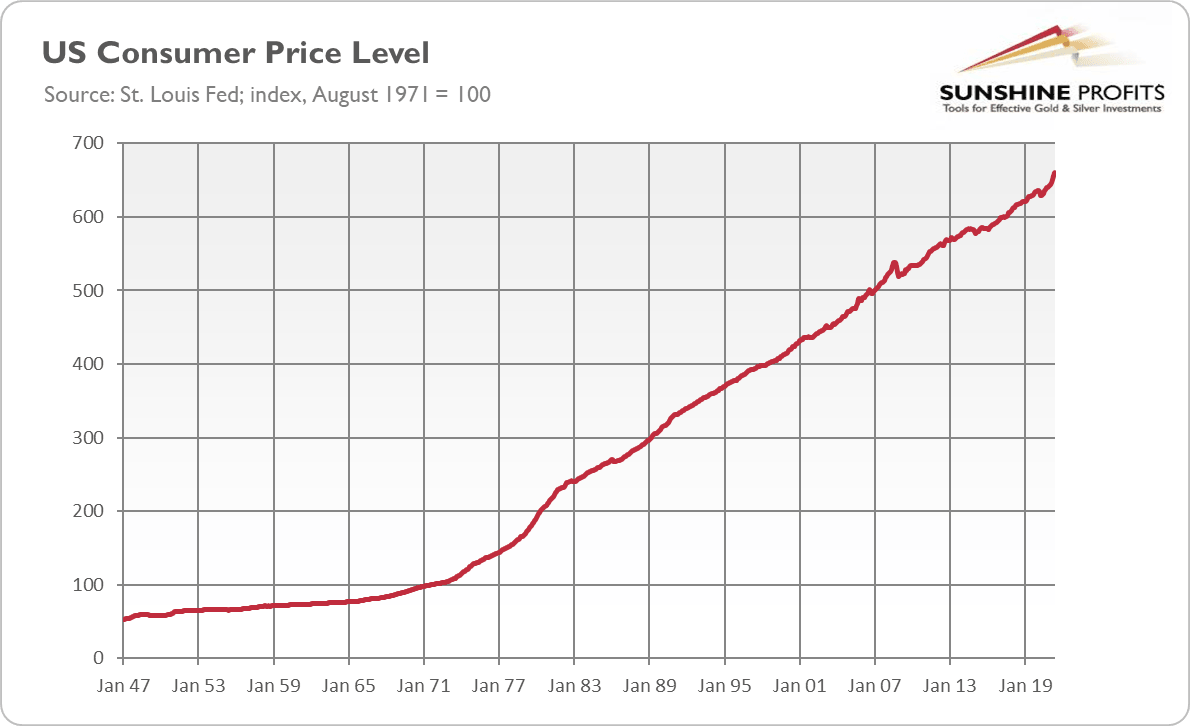
Well, it didn’t work out as planned. The greenback plunged by a third during the 1970s. It also lost a lot of its domestic purchasing power. The average annual inflation rate between August 1971 and May 2021 was almost 4%, generating a cumulative price increase of about 560%. Indeed, as the chart below shows, the Consumer Price Index is now 6.6 times higher than in mid-1971.
It means that $1 then is equivalent in purchasing power to about $6.6 today, an increase of $5.6. In other words, a dollar today only purchases less than 18% of what it could buy back then (so, it has lost more than 82%of its purchasing power since 1971). So much about curbing inflation and stabilizing the dollar.
Other promises have also been broken. The unemployment rate was, on average, higher, while the GDP growth was slower in the period after 1971. And since Nixon terminated the gold standard, there have been a lot of financial instability and several economic crises, including the stagflation in the 1970s and the global financial crisis in 2008-09.
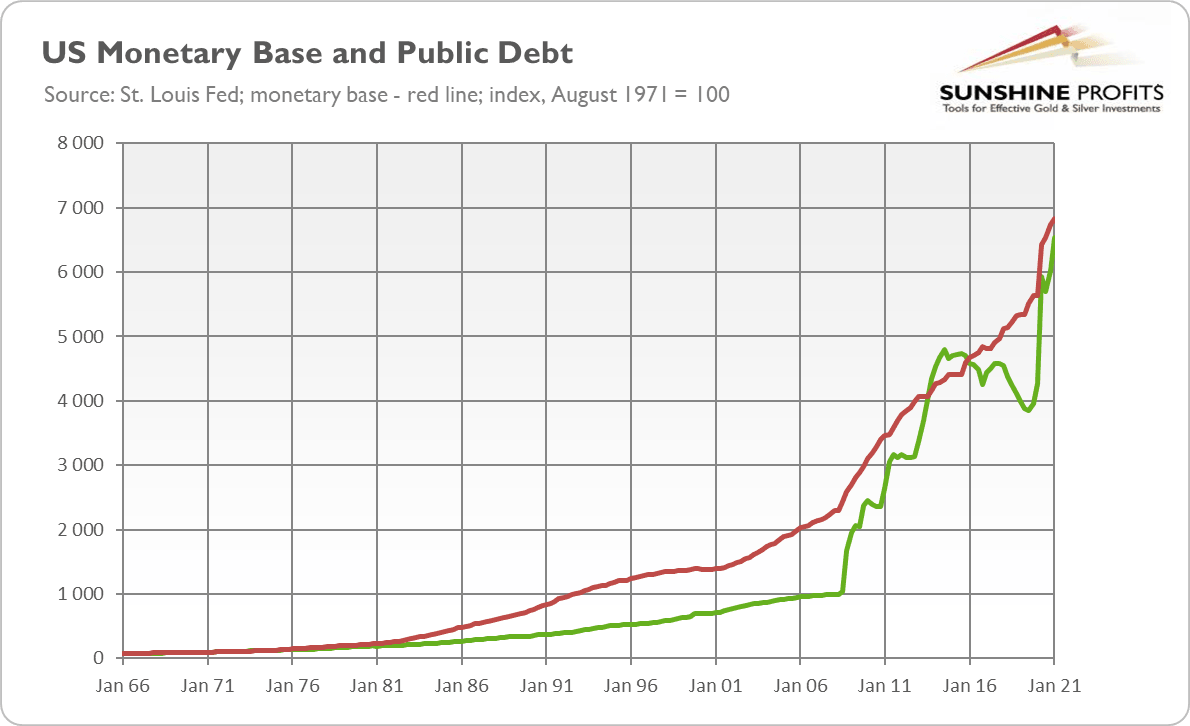
The post-1971 monetary system was good at only one thing: at boosting the money supply and the public debt. Without the gold anchor, the Fed could create money (as well as the Treasury) and spend it more freely than under the gold standard. Indeed, as the chart below shows, both the monetary base and the federal debt have accelerated since the 70s, surging to a level about 650 times greater.
Hence, the closure of the gold window still has an impact on the global economy and the precious metals markets. If gold continued to serve as the ultimate money, monetary and fiscal policies would be more rational and the public debt wouldn’t exceed 100% of GDP in peacetime.
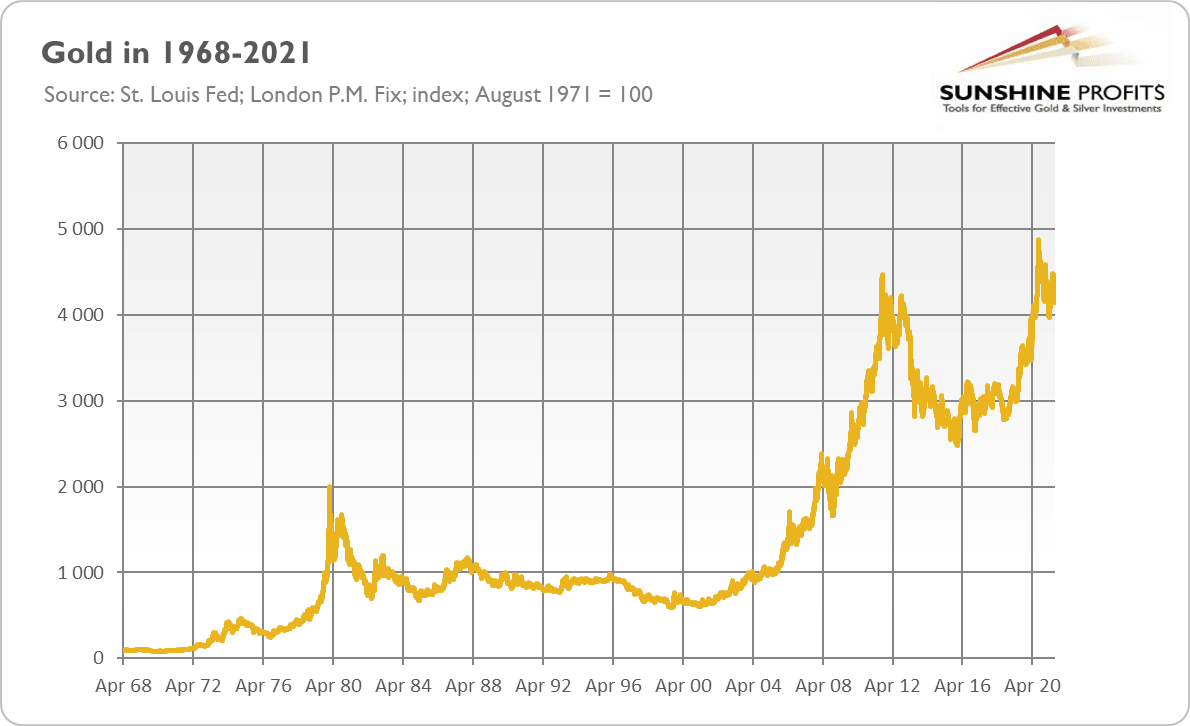
It means that the lack of the gold standard is, somewhat paradoxically, good for gold prices. When Nixon killed the Breton Woods, some analysts claimed that the price of the yellow metal would decline without being linked to the dollar. As we all know, and as the chart below shows, the opposite happened.
Over the past fifty years, the price of gold has soared about 4100% – or more than 7.7% annually, on average. Additionally, given all the instabilities present in the contemporary monetary system based on fiat currencies, unlimited money-printing and monetization of debt, in the long run, the price of gold may only continue its upward trend.
Want free follow-ups to the above article and details not available to 99%+ investors? Sign up to our free newsletter today!
Want free follow-ups to the above article and details not available to 99%+ investors? Sign up to our free newsletter today!
Author

Arkadiusz Sieroń
Sunshine Profits
Arkadiusz Sieroń received his Ph.D. in economics in 2016 (his doctoral thesis was about Cantillon effects), and has been an assistant professor at the Institute of Economic Sciences at the University of Wrocław since 2017.