Gold price extends steady intraday descent, tests $3,370-3,365 hurdle-turned-support
- Gold price attracts some follow-through selling as trade optimism undermines safe-haven demand.
- A modest USD bounce from a two-week low further contributes to the commodity's corrective slide.
- The Fed rate-cut uncertainty might cap the USD and limit losses for the non-yielding yellow metal.

Gold price (XAU/USD) continues to lose ground through the first half of the European session and drops to the $3,365 hurdle-turned-support zone in the last hour. The latest optimism over the US-Japan trade deal, along with reports that the US and the European Union (EU) are closing in on a tariff deal, remains supportive of the upbeat market mood. This, in turn, is seen as a key factor exerting downward pressure on the safe-haven bullion for the second consecutive day.
Meanwhile, the US Dollar (USD) attracts some buying and, for now, seems to have snapped a three-day losing streak to a two-week low, which contributed to driving flows away from the Gold price. Any meaningful USD recovery, however, seems elusive amid the uncertainty over the Federal Reserve's (Fed) rate-cut path. Moreover, concerns about the US central bank's independence might cap the USD recovery and offer some support to the non-yielding yellow metal.
Daily Digest Market Movers: Gold price bears retain control amid fading safe-haven demand, rebounding USD
- US President Donald Trump announced late Tuesday that his administration had reached a trade deal with Japan. Furthermore, reports that the US and the European Union are heading towards a 15% trade deal boost investors' confidence and weigh on the safe-haven Gold price for the second straight day on Thursday.
- The markets do not expect an interest rate cut from the US Federal Reserve in July despite Trump's continuous push for lower borrowing costs. In fact, Trump has been attacking Fed Chair Jerome Powell personally over his stance on holding rates and repeatedly calling for the central bank chief's resignation.
- Moreover, Fed Governor Chris Waller and Trump appointee Vice Chair for Supervision Michelle Bowman have advocated a rate reduction as soon as the next policy meeting on July 30. This keeps the US Dollar depressed near a two-and-a-half-week low and could offer some support to the non-yielding yellow metal.
- Traders now look forward to the release of flash PMIs, which would provide a fresh insight into the global economic health and influence the safe-haven commodity. Apart from this, the crucial European Central Bank policy decision might infuse some volatility in the markets and drive the XAU/USD pair.
- Meanwhile, the US economic docket features Weekly Initial Jobless Claims and New Home Sales data, which, in turn, would drive the USD and contribute to producing short-term trading opportunities around the commodity. Nevertheless, the fundamental backdrop warrants caution for aggressive traders.
Gold price flirts with the $3,370 pivotal resistance-turned-support; dip-buying should help limit further losses
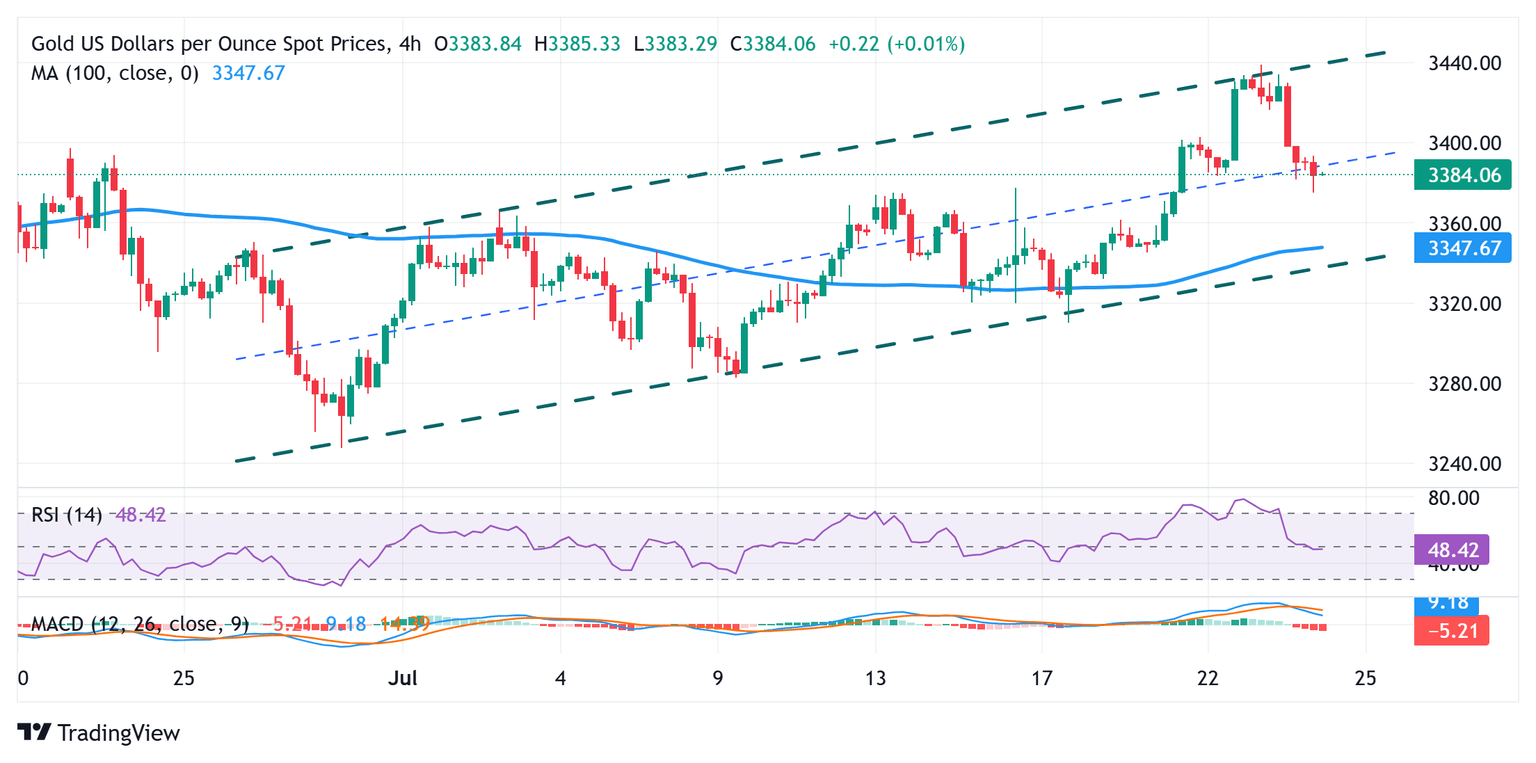
From a technical perspective, the recent move up along an upward sloping channel since the beginning of this month points to a well-established short-term uptrend. Adding to this, positive oscillators on the daily chart suggest that the Gold price is more likely to find decent support near the $3,370-3,368 strong horizontal resistance breakpoint. A convincing break below the said area, however, could expose the lower end of the trend-channel, currently pegged near the $3,333-3,332 region. The latter should act as a key pivotal point, which if broken decisively might shift the near-term bias in favor of the XAU/USD bears.
On the flip side, momentum back above the $3,400 mark could pause near the $3,438-3,440 static barrier. This coincides with the trend-channel resistance, above which the Gold price could accelerate the positive move towards challenging the all-time peak, around the $3,500 psychological mark touched in April.
Fed FAQs
Monetary policy in the US is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these goals is by adjusting interest rates. When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% target, it raises interest rates, increasing borrowing costs throughout the economy. This results in a stronger US Dollar (USD) as it makes the US a more attractive place for international investors to park their money. When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates to encourage borrowing, which weighs on the Greenback.
The Federal Reserve (Fed) holds eight policy meetings a year, where the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) assesses economic conditions and makes monetary policy decisions. The FOMC is attended by twelve Fed officials – the seven members of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the remaining eleven regional Reserve Bank presidents, who serve one-year terms on a rotating basis.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve may resort to a policy named Quantitative Easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is a non-standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy high grade bonds from financial institutions. QE usually weakens the US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process of QE, whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing, to purchase new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US Dollar.
Author

Haresh Menghani
FXStreet
Haresh Menghani is a detail-oriented professional with 10+ years of extensive experience in analysing the global financial markets.

















