Geopolitics in the future US dollar trends
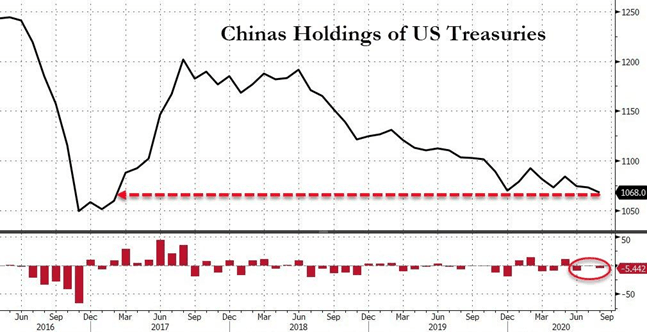
Recent news about China's sale of U.S. Treasuries and a significant increase in its holdings of Japanese Government Bonds (JGBs) has caught the market's attention. China cut its holdings of U.S. Treasuries by USD 5.4 billion to USD 1.07 trillion in August, its third straight month of selling, making its total holdings of U.S. Treasuries fell to the lowest level in more than three years. Compared to August 2017, when it held more than USD 1.2 trillion in U.S. Treasuries, China has reduced its U.S. Treasuries holdings by USD 130 billion. Meanwhile, China has been buying more JGBs in 2020, the highest amount in three years. During April and July this year, China continued to buy JPY 1.46 trillion of medium- to long-term JGBs.
Figure 1: Changes in China's holdings of U.S. Treasuries
JGBs are low-return bonds with almost zero yield, which is also the main reason why European countries have been reducing their holdings of JGBs this year. In terms of investment, China's massive purchase of low-yielding JGBs while dumping U.S. Treasuries is certainly not a rational investment move. So, why did China make such a move?
Against the backdrop of a dramatic deterioration in the geopolitical situation, China's adjustment of its holdings of U.S. Treasuries and JGBs could easily be linked to geopolitics. There is some truth to this view. At present, the international geopolitical and geo-economic situation has changed dramatically, and U.S.-China relations have become the focus of contradictions. China needs to expand its economic and trade ties, and Japan is one of the key economic partners that China needs to improve its relations with (for more details, please refer to the "1+3" concept put forward by ANBOUND). A modest increase in China's holdings of JGBs is clearly in line with today's geopolitical needs. China's adjustment of its foreign government bond holdings in recent months can be seen as a "repositioning" of its foreign assets with geopolitical significance.
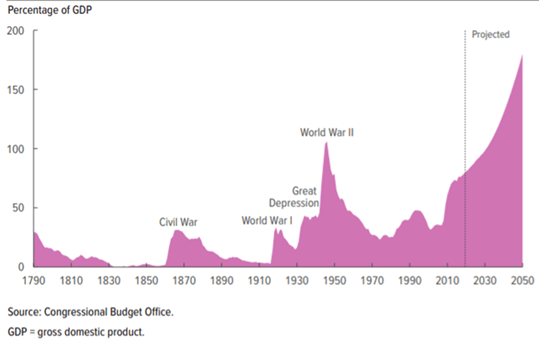
Concerns about the potential risks to the U.S. dollar and U.S. debt could be another important reason for China to restructure its foreign bond holdings. To cope with the impact of COVID-19, the U.S. greatly expanded its deficit. As of October 20, more than 8.45 million COVID-19 cases and 225,000 deaths had been confirmed in the United States, the country with the largest number of cases in the world. The U.S. Department of Treasury on Thursday released its final budget for the fiscal year 2020, which ends on September 30, with a record deficit of USD 3.1 trillion. The U.S. fiscal deficit also rose to 15.2% of GDP from 4.6% in the previous fiscal year, the highest level since 1945. The U.S. Congress estimates that increasing deficits will push U.S. federal debt to very high levels over the next 30 years, possibly reaching 195% of GDP by 2050.
Figure 2: U.S. Congressional estimates of the debt-to-GDP ratio
The continued increase in U.S. debt is nothing new, but what worries the markets is the expansion of U.S. debt becomes unsustainable. To make up for the federal deficit, U.S. debt will swell uncontrollably. The U.S. will need to sell more U.S. Treasuries to global investors to hedge against its USD 3 trillion deficit. Once the U.S. debt is not favored by the market, or if it continues to be undercut by the market, the U.S. deficit economic model will not be sustainable. In the wake of the COVID-19 outbreak, the U.S. increased its issuance of bonds, which also accelerated the process of risk accumulation. The Fed's continuous loosening policy could damage the dollar in terms of its quantitative to qualitative, bringing financial market volatility and even crisis. Now the capital market is worried that the U.S. economy and capital market cannot do without the loose policy from the Fed. The Fed's monetary policy is de facto ineffective due to near-zero interest rates, low inflation, and rising debt. If inflation picks up in the future, the Fed's attempts to raise interest rates will burst the market bubble.
The fear of financial risk in the United States actually involves a critical judgment, i.e., is the dollar dead and a financial crisis inevitable? According to Chan Kung, chief researcher at ANBOUND, it is important to make clear this critical judgment, which will influence a country's strategy of holding foreign debt and allocating foreign exchange reserves. Even the World Bank has now judged that the U.S. loose policy will lead to a financial crisis, which will also lead to a significant depreciation of the dollar.
However, ANBOUND holds a different judgment on the long-term prospects of the dollar. According to the theory of "geo-capitalism" put forward by Chan Kung, modern geopolitics is actually geo-capitalism, and behind space there are strong monetary and financial motives. The economic crisis and the competition for space advantage are driven by capital, and the ability to monopolize or control market space is in fact the foundation of currency and finance. From this perspective, as long as the geopolitical power of the U.S. does not collapse, the position of the dollar will not collapse, which means that there will not be profound and major volatility in the dollar for a considerable period of time. On this basis, the dollar is not heading for sustained and substantial depreciation, and the current short-term market volatility does not represent a medium- to long-term trend.
A country's decisions and actions could be very different as a result of different key judgments. If the medium- and long-term status of the U.S. dollar is deemed to change, then a substantial reduction in the holdings of U.S. dollar assets, including U.S. treasuries, is likely to cause real losses, turning paper losses brought about by short-term fluctuations into real losses.
Analysis of the positions of the U.S. dollar and the Japanese yen in geo-currency terms draws interesting conclusions. According to Chan Kung, from the perspective of geopolitics, the Japanese yen is not completely independent from the U.S. dollar, it has a certain "dollar attribute", which depends in part on the performance of the U.S. dollar. A country that still has a large number of U.S. troops stationed is not a fully independent normal country. To say that Japan's currency can completely deviate from the dollar is actually against the logic of geopolitics. In other words, the fact that Japan is not geopolitically independent is also reflected in its currency.
Final analysis conclusion
Is China's reallocation of its holdings of U.S. Treasuries and JGBs a strategic adjustment? This involves a critical judgment of the dollar's medium- to long-term trend. A directional error in critical judgment is likely to result in a loss of asset allocation. Moreover, the "independence" of the Japanese yen to the dollar should not be overestimated, as the Japanese yen is somewhat correlated with the dollar due to geopolitical influences.
Author

ANBOUND Team
ANBOUND Research Center Sdn Bhd