Africa in the Westphalian system

Before the modern era with it’s legally recognised states the world had political entities of all types ranging from the tribe to the empire to the Caliphate which fulfilled more or less the same functions. However in the post 1945 period a State is a specific legal entity that may or may not correspond to any historical construction.
In sub-Saharan Africa in the nineteenth century the European colonial powers divided up the Continent according to their own logic with little regard for any local political structures which had existed previously. Then in the post-war period when colonial holdings became untenable the European divisions became independent states (Westphalian States) and this had all sorts of unintended consequences.
On independence the Europeans handed over institutions which mirrored their own to local rulers in the expectation that these would allow modern states and modern economies to emerge. However this has not happened and if we look a little beneath the surface we can easily understand why not. Each individual is part of a society and that society is what he or she has known to have existed historically with it’s language, culture, traditions and political structure. In Africa most such societies were tribal. During the European period political institutions were created to serve the European powers for purposes such as, for example, mineral extraction and infrastructure was created to serve the European interests.
On independence very few of the local populations would have had any concept of belonging to the colonial state. In many cases tribes were not really aware of being colonised as the colonial structures barely affected them. By creating states that threw many different tribes together and, in some cases dividing tribes between states, the departing colonial powers left behind institutions that were incomprehensible to the locals. Because these states were internationally recognised that had several consequences for the distribution of power within them. Only the state was legally allowed to trade externally. Only the state had the power to issue currency and raise taxes.
The tribal political culture is essentially monarchical and in Europe the transition from monarchical rule to representative parliamentary systems took several centuries and evolved in tandem with economic and societal development. In Africa it is hardly surprising that the institutions left behind by the Europeans rapidly fell by the wayside. What tended to happen is that the individuals who inherited power from the Europeans rapidly tended to become autocratic because the political culture they knew was monarchical. They also tended to favour their own tribe and this created resentment among other tribes.
There were also a number of other issues that affect to the functioning of a modern state:
-
How widespread is literacy and education.
-
Which language serves as a lingua franca (usually the language of the former colonial power) and how widely is this spoken.
-
Skills and training required in the operation of international businesses in mining and agriculture.
-
The creation of the permanent institutions of a State covering everything from administration to security.
All of these factors made the states very difficult to govern and, in fact, the institutions left behind by the departing colonial powers tended to induce civil war rather than stability. This was exacerbated by the Cold War rivalry between the US and the USSR who supported their own clients and it also led to the widespread proliferation of modern weaponry with disastrous consequences.
Several decades on we are in a situation where these states have achieved an air of permanence and as the tribal structures become less relevant individuals have started to see their futures in terms of the state and started to make them work.
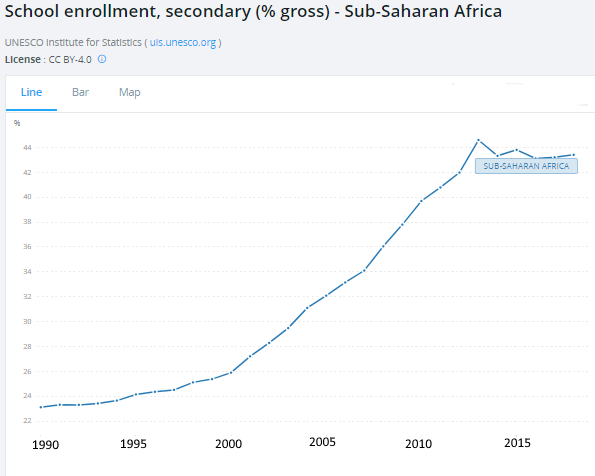
Primary schooling is near universal and it can be seen that almost half the population now attend secondary education.
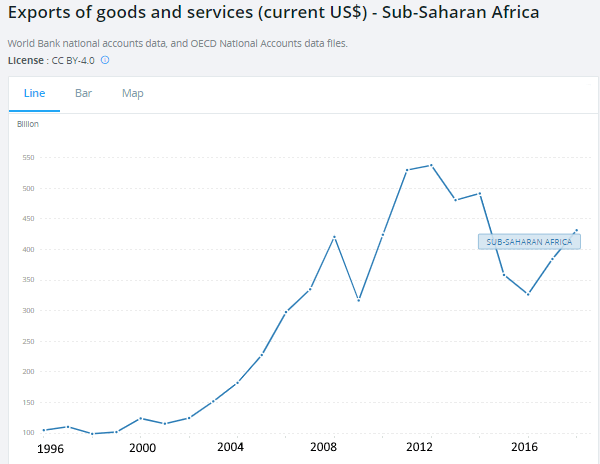
Exports have grown strongly since the Millennium due to the emergence of China, and to a lesser extent India, as major export markets. Export growth has stalled in recent years but this is mostly due to the fluctuations in world market prices of commodities. The expansion of exports together with improved governance will allow for African economies to continue to grow.
Author

Paul Dixon
Latin Report
Paul Dixon’s focus is economics from a long term perspective.