Haiti and the dominican republic

Hispaniola was the first island in the Americas settled by the Spanish and the cathedral of Santo Domingo is the hemisphere’s oldest. After 1625 the French gained control of the western side of the island and established a sugar plantation economy based on black slave labour. In 1791 a slave rebellion broke out as France was in the midst of it’s own revolution and this was initially supported by the Spanish from their side of the island.
This led in 1792 to the official abolition of slavery and a pledge of allegiance by the rebel leader Toussaint l’Ouverture to France. However the situation remained unsettled and eventually reinforcements were sent from France to reestablish control but most of these quickly succumbed to tropical illnesses from which they had no immunity and the remaining forces were routed such that Haiti (which was the island’s indigenous name) attained it’s independence in 1804. This was the first and only successful slave rebellion in the Western Hemisphere which resulted in statehood.
However from such a promising start the outcome was underwhelming. Most of the French community were driven off the island (with many founding sugar plantations in Cuba) and no matter the motives behind this reaction it had the effect of cutting Haiti off from the main trading and cultural currents in the region such that it was unable to lift it’s economy onto a sustainable basis. Another factor working against the new state was the refusal of the United States to recognise it (and thus establish trading relations) , because it had a black government, until after the abolition of slavery in the US in 1865.
The Spanish part of the island had been occupied by both France and the slave armies for brief periods during the French revolutionary wars. This was soon followed by the upheavals all over Spanish America against Spanish rule and after several years independence was declared in 1821. However the newly independent republic was almost immediately occupied by Haiti and only became independent in 1844.
In 1915 the US occupied Haiti in order to forestall a possible intervention there by the German Imperial Navy and they remained until 1934. This 19 year “trusteeship” was a period of material progress – 1,000 miles of road and 200 bridges were built financed from locally raised taxes. The US Pentecostal Churches became established there and there was the emergence of a mostly Milat (mixed race) middle class. In spite of the economic advances the US occupation was widely resented and in the post-occupation period a literary/intellectual movement emerged known as noirisme (or blackness) one of whose leading members was Francois Duvalier (Papa Doc). Noirisme exalted black culture and traditions such as Vodoo above European imports and regarded Western Institutions as alien.
When Duvalier came to power in 1957 he thus rejected institutions that might have led to social progress and established a reign of terror supported by militias (the Tonton Macoutes) reporting directly to him. This drove much of the educated Milat class into exile and discouraged international companies from operating there with the effect that the economy suffered several decades of stagnation.
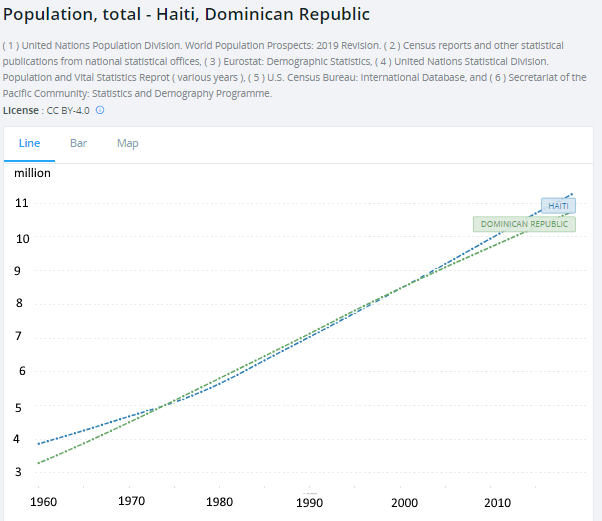
It can be seen that both parts of the island have had similar population trajectories since the 1960’s.
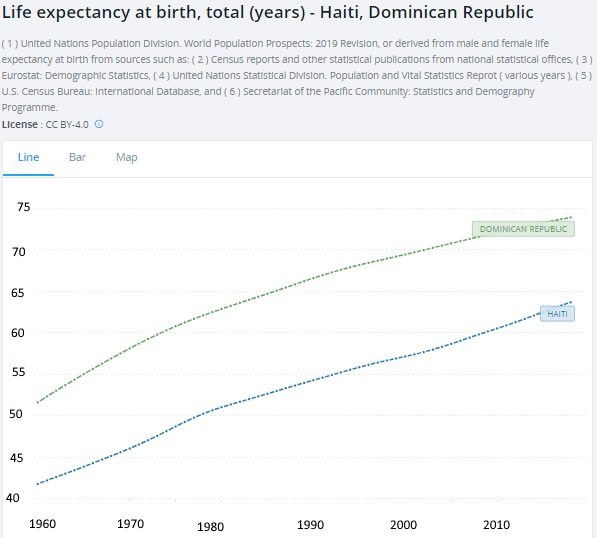
Life expectancy in the Dominican Republic has reached 74 years and 64 years in Haiti. It is significant that life expectancy in Haiti shows continuous improvement in spite of all of it’s problems. Also note that whereas the Dominican Republic has a literacy rate greater than 90%, in Haiti it is about 62% but if we break this latter statistic down it will be seen that the literacy rate for young perople is above 80%. Also note that in Haiti mobile phone penetration is near universal and texting (which assumes literacy) widespread.
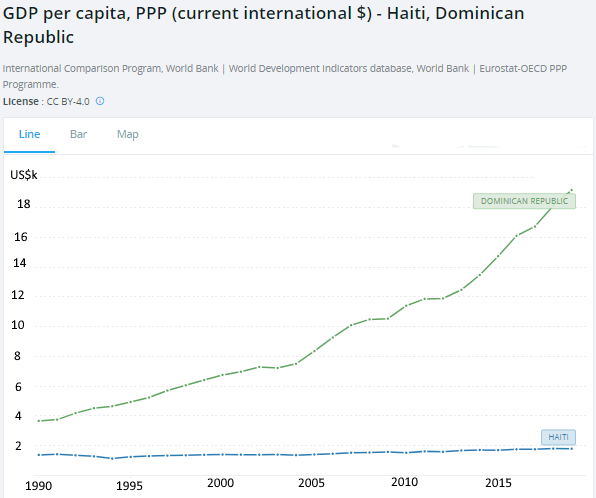
It can be seen from the graph that the Dominican Republic has been on a strongly upward trajectory since 1990 whereas Haiti shows only modest progress. The Dominican economy is based mostly on tourism and Zonas Francas (free ports where manufacturing inputs can be imported customs free and then the end product exported). There was a sharp contraction in 2003 due to the collapse of Banco Intercontinental but for decades the Dominican economy has grown at an average of 5% per annum which is very stable. It’s tourism will suffer a major contraction this year but paradoxically Haiti will be less affected.
Author

Paul Dixon
Latin Report
Paul Dixon’s focus is economics from a long term perspective.